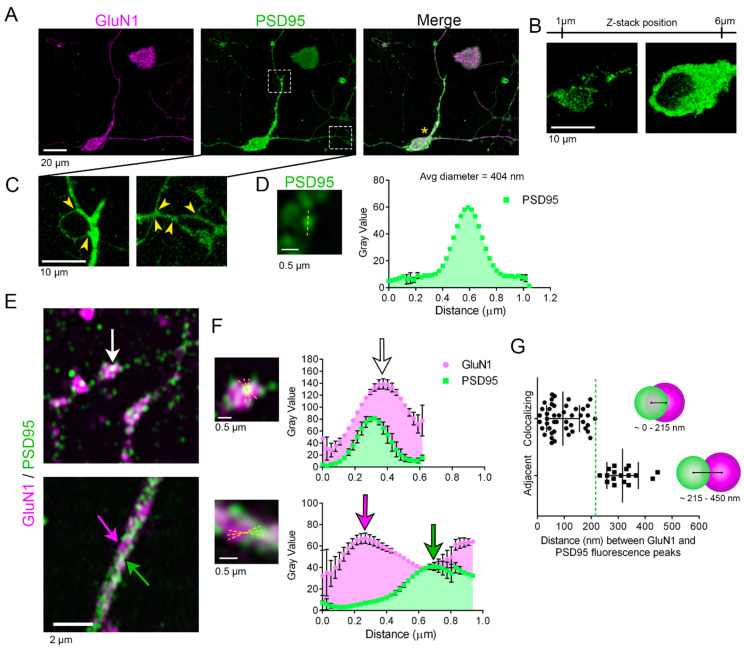
Figure 1.
Hypothalamic neurons in primary culture express GluN1 localized at postsynaptic sites. (A) An orthogonal projection of six confocal images of a primary neuron expressing endogenous GluN1 and PSD95 visualized with the rabbit anti-GluN1 (AGC-001) and anti-PSD95 K28/43 antibody, respectively. The white rectangles indicate the inset regions shown at higher magnification in (C), and the yellow asterisk indicates the neuron of interest. (B) Left and right panels: Single confocal images from different positions of a Z-stack of 6 µm thickness showing the punctate distribution of PSD95 (left) and the negative staining of the nucleus (right) in the cell soma of the neuron shown in (A). (C) Enlarged images of the inset regions in (A). Yellow arrowheads indicate branching points. (D) A representative SR image of a point of PSD95 fluorescence with a representative yellow dashed line was used to determine the average diameter of PSD95 points. The graph on the right illustrates the average +/− SEM fluorescence (gray value) of PSD95 along the line, determined by measuring 180 spots of PSD95 fluorescence from 6 neurons. (E,F) SR images of a neurite expressing GluN1 and PSD95. The white arrow indicates a spot of PSD95 and GluN1 colocalization, and the green/magenta arrows indicate spots where PSD95 and GluN1 are adjacent. The regions indicated by the arrows are shown enlarged in (F). Yellow lines indicate those drawn for line segment analyses, with corresponding graphs displayed as means +/− SEM. (G) The distance (nm) between GluN1 and PSD95 fluorescence peaks was determined by the line segment analyses from 6 neurons from 2 independent experiments (n = 46 colocalizing points, n = 17 adjacent points), displayed as means +/− SD. The green dotted line is placed at the 216 nm cutoff that discriminates spots at which GluN1 and PSD95 colocalize (distance of fluorescence peaks < 216 nm) and those where GluN1 and PSD95 are adjacent (distance between fluorescence peaks > 216 nm and <450 nm), as indicated by the models.