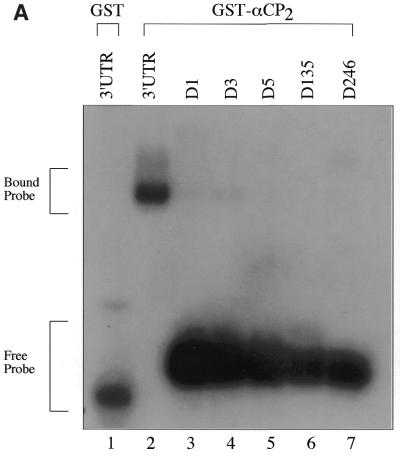
Figure 4.
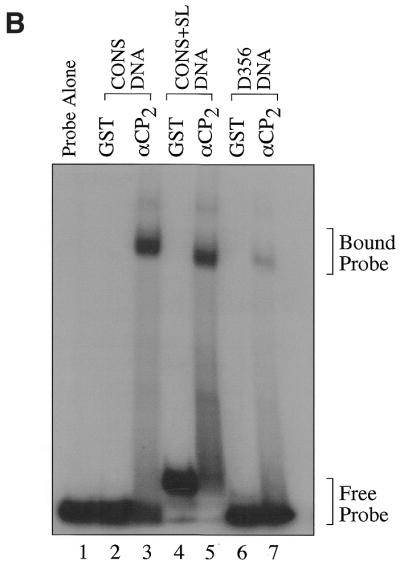
GST–αCP2 specifically binds 3′-UTR DNA sequences. (A) RNA sequences containing point mutations in the C triplets present in the 3′-UTR were generated as described in Materials and Methods. These were used in EMSA reactions to determine if the base changes affected binding of αCP2. The point mutations resulted in a >95% decrease in binding by αCP2, indicating a very high sequence specificity in the EMSA reactions. (B) Radiolabeled DNA was synthesized by phosphorylating 200 ng ssDNA using polynucleotide kinase and [γ-32P]ATP. The probes were gel purified and 15 000 c.p.m. were used per reaction. The 3′-UTR DNA binds specifically to GST–αCP2 (lanes 2 and 3). The addition of a stem–loop sequence to the ends of the 3′-UTR sequence did not affect binding to GST–αCP2 (lanes 4 and 5). Mutations in three of the C triplet repeats caused an 80% reduction in binding the DNA (lanes 6 and 7).