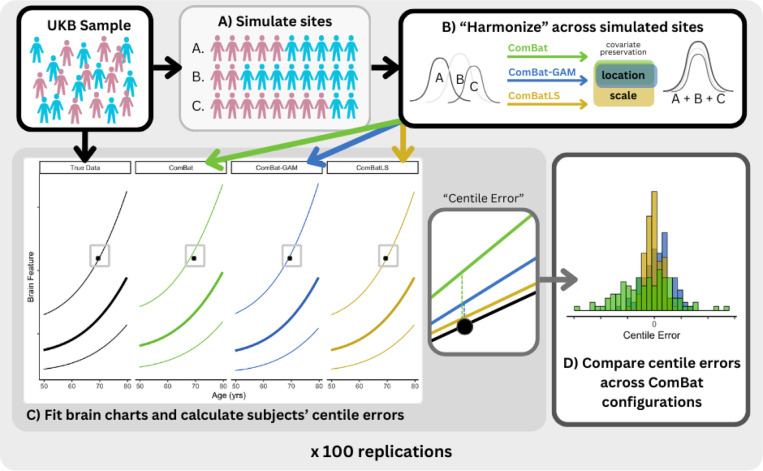
Figure 1. Summary of Methodological Approach.
A) Subjects from the UK Biobank (UKB) sample are randomly assigned to one of 3 simulated “study sites” such that sites have a Male:Female ratio of 1:1, 1:4, or 4:1. B) Brain structure feature data are “harmonized” across these simulated sites using different configurations of ComBat, preserving covariates’ effects on the mean (ComBatLS, ComBat-GAM, linear ComBat) and/or variance (ComBatLS). C) Brain growth charts are fit for brain features using the original true structural data and data harmonized by each ComBat pipeline, which are then used to calculate personalized centile scores describing each subject’s percentile relative to the population distribution. Centile error, defined as the difference between a subject’s centile score when benchmarked on a brain chart modeled on “true” data and one fit on ComBat-harmonized data, was calculated for each brain feature across all subjects. Lines represent brain charts of the 75th, 50th, and 25th percentiles for the feature given age; the solid point represents a single subject’s brain feature, which has a “true” centile of 75% but corresponds to different centile scores when data is harmonized. D) We analyzed the distributions of centile errors within and between ComBat configurations to assess the degree to which each harmonization method preserved biological variability in the simulated sites, thus minimizing centile errors.