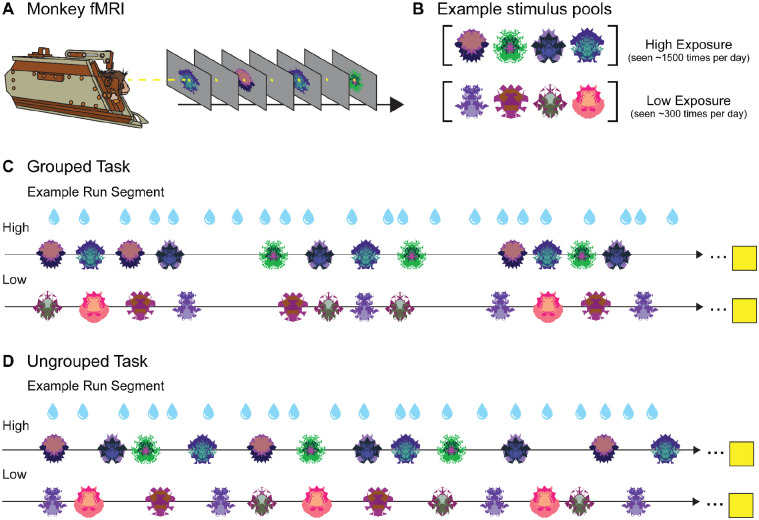
Figure 1. No-report Grouped and Ungrouped viewing tasks.
A. Monkeys in “sphynx” position fixate on central fixation square during fMRI scanning for both tasks. B. Example High and Low Exposure stimulus pools for both Ungrouped and Grouped tasks depict images that would be used for a single scanning session. Over the course of a standard scanning session, High Exposure images will be presented ~1500 times on average while Low Exposure images will be presented ~300 times on average. C. Example partial Grouped task run showing two of three possible block types (snippets of High and Low Exposure blocks are shown, the third deviant block type is not reported here). Three pseudorandomized four-item example groupings are shown for a High Exposure block (top row) and Low Exposure block (bottom row). Four-item image groups appear in six possible timing templates. All blocks contained 30 four-item groupings (120 total image presentations). The yellow square indicates the 14 second fixation period between each block. D. Example partial Ungrouped task run showing snippets of High and Low block types (the third is not shown). Twelve pseudorandomized image presentations with jittered timing are shown for a High Exposure block (top row) and Low Exposure block (bottom row). All blocks contained 120 image presentations. The yellow square indicates the 14 second fixation period between each block. Blue water droplets schematize reward delivery, which is decoupled from image events and delivered on a graduated schedule based on the duration the monkey has maintained fixation.