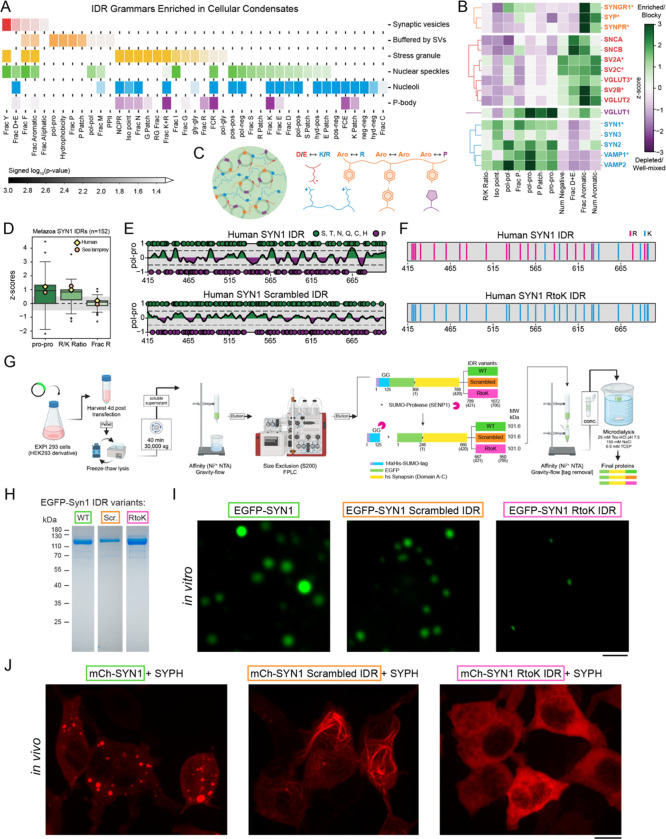
Figure 1: IDRs of proteins that make up synaptic condensates feature distinct molecular grammars.
A. IDR grammars of SV proteins are distinct from those of IDRs in other condensates.
B. IDR compositions and sequence patterns of pre-synaptic proteins fall into distinct clusters.
C. Schematic illustrating the chemical complementarity across IDRs within SV clusters.
D. Molecular grammars are conserved across 152 metazoans, including lamprey, which is the oldest vertebrate predecessor of humans.
E. Schematic showing how the synapsin-1 scrambled IDR in which polar and proline blocks are evenly distributed to reduce blockiness.
F. Schematic of the synapsin-1 IDR showing the substitution of Arg with Lys.
G. Purification protocol for synapsin-1 IDR (WT) and the two variants SCR and RtoK.
H. Coomassie gel indicating the final recombinant proteins used for the biophysical assays.
I. Microscopy images of EGFP-synapsin-1 (8 μM) with WT, SCR, and RtoK IDR reconstituted in 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.5 mM TCEP, 150 mM NaCl and 3% PEG 8,000. Scale bar, 5 μm.
J. Images of HEK cells expressing EGFP-synapsin-1 WT (left), EGFP-synapsin-1 scrambled IDR (middle), or EGFP-synapsin-1 RtoK IDR (right) with untagged synaptophysin. Mutants disrupted formation of normal synapsin condensates. IDR scramble formed filaments resembling cytoskeleton, and RtoK completely abolished condensation. Scale bar, 10 μm.