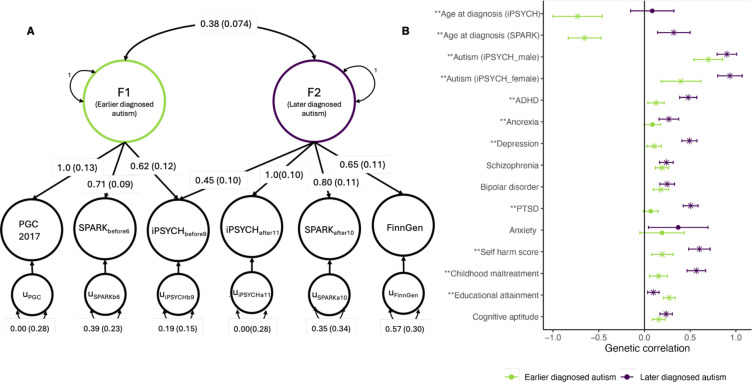
Figure 5: Two genetic latent factors in autism.
A. Path diagram illustrating the two-correlated-genetic-factor models for autism, using six minimally overlapping autism GWAS datasets. F1 = Factor 1, F2 = Factor 2. One-headed arrows depict the regression relationship pointing from the independent variables to the dependent variables. The numbers are the regression coefficients of the factor loadings, with the standard errors provided in parentheses. Covariance between variables are represented as two-headed arrows linking the variables. The numbers on the two-headed arrows can be interpreted as genetic correlation estimates with the standard errors provided in parentheses. Residual variances are represented using a two-headed arrow connecting the residual variable (u) to itself. Standard errors are provided in parentheses. B. Genetic correlation between the two autism factors and a range of mental health, neurodevelopmental, and cognitive traits. Points indicate the estimate, whiskers indicate 95% confidence intervals, and points with an asterisk (*) indicate significant associations with Benjamini-Yekutieli adjustment. Two asterisks (**) indicate phenotypes where the difference in genetic correlation between earlier and later diagnosed autism is statistically significant at P < 0.05.