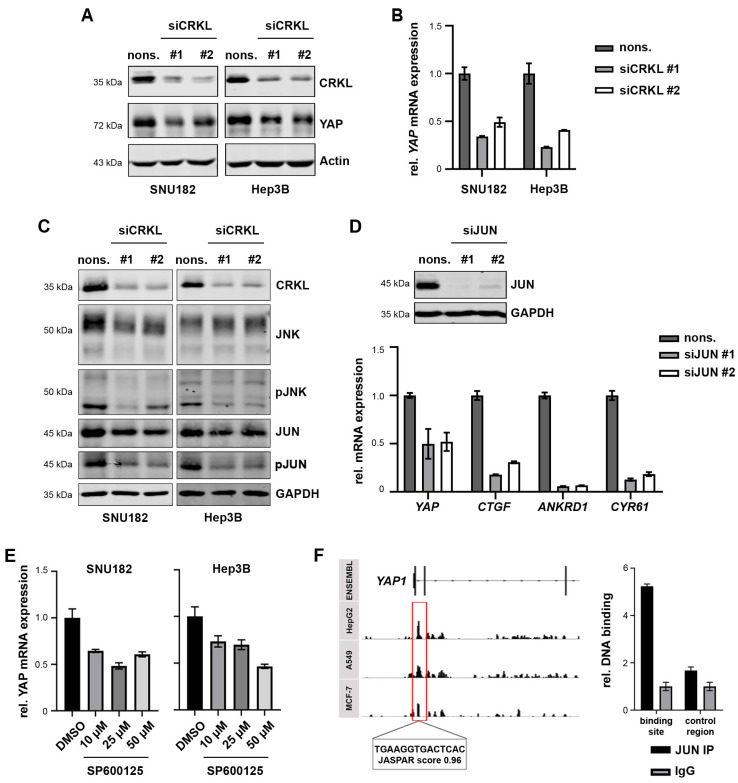
Figure 5.
CRKL activates JNK/JUN to induce YAP transcription. (A) The inhibition of CRKL reduced the YAP protein level, as shown by Western Immunoblot. Actin served as the loading control. (B) The YAP mRNA level was decreased after the knockdown of CRKL, as measured by real-time PCR. (C) CRKL inhibition reduced the phosphorylated JNK (pJNK) and JUN (pJUN) levels, as shown by Western Immunoblot. GAPDH served as the loading control. (D) SiRNA-mediated knockdown of JUN led to a reduction in YAP mRNA, as well as a reduction in the target gene expression, as shown by real-time PCR. (E) Treatment with the JNK inhibitor SP600125 for 24 h reduced YAP expression, as illustrated by real-time PCR. DMSO served as control. (F) The scheme shows JUN ChIPseq peaks at the genomic YAP locus for three different cell lines from the ENCODE project. A predicted JUN binding site is highlighted. The bar graph shows the results from JUN ChIP with the amplification of the predicted binding site compared to IgG precipitation and a negative downstream control region. For siRNA transfection, nonsense siRNAs (nons.) served as controls.