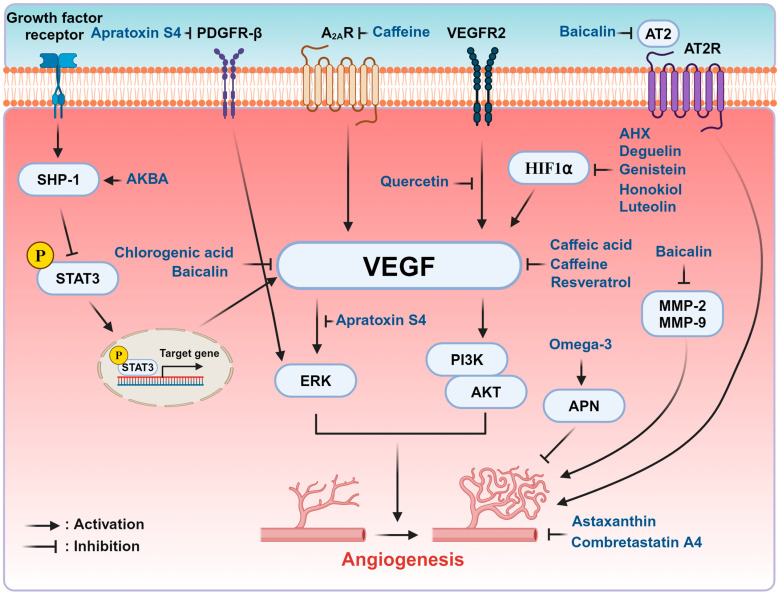
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of Natural Products in the progression of ROP. The Regulatory mechanisms of natural compounds discussed in this article are demonstrated at the cellular level. Natural compounds act as inhibitors of angiogenesis by regulating angiogenesis-related receptors or engaging various signaling pathways. Activation is indicated by pointed arrows, while inhibition is represented by T-bars. Abbreviations: AHX, 2-Azahypoxanthine; AKBA, acetyl-11-keto-b-boswellic acid; A2AR, adenosine A2A receptor; APN, adiponectin; AKT, protein kinase B; AT2R, angiotensin II receptor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; HIF1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PDGFR-β, platelet-derived growth factor β; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SHP-1, Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.