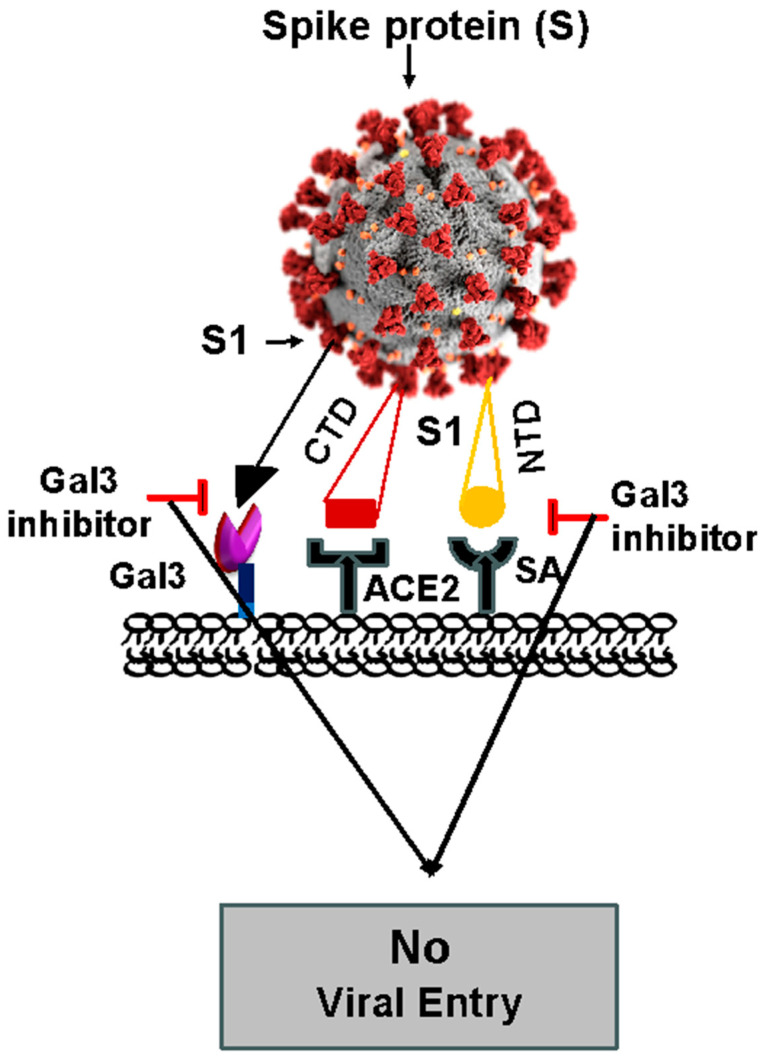
Figure 4.
Schematic representation showing virus–host cell interactions and Gal3 inhibition blocking viral entry to host cells. Gal3 is believed to play critical role in viral entry to host cells. Interaction between the galectin-like S1-NTD (N-terminal domain of the virus S1 spike protein) and host sialic acids could be critical for viral entry as means of stabilizing the interaction between S1-CTD (C-terminal domain of the virus S1 spike protein) and ACE2. Moreover, host Gal3 may participate in additional interactions with virus spike glycoprotein for further stabilization, contributing to prolonged infection and severity of disease. Therefore, Gal3 inhibition may disrupt attachment of SARS-CoV-2 to cell surface, preventing entry to host cells (adapted from Refs. [72,80]). The SARS-CoV-2 image was taken from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website (https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/86942, access on 20 May 2024).