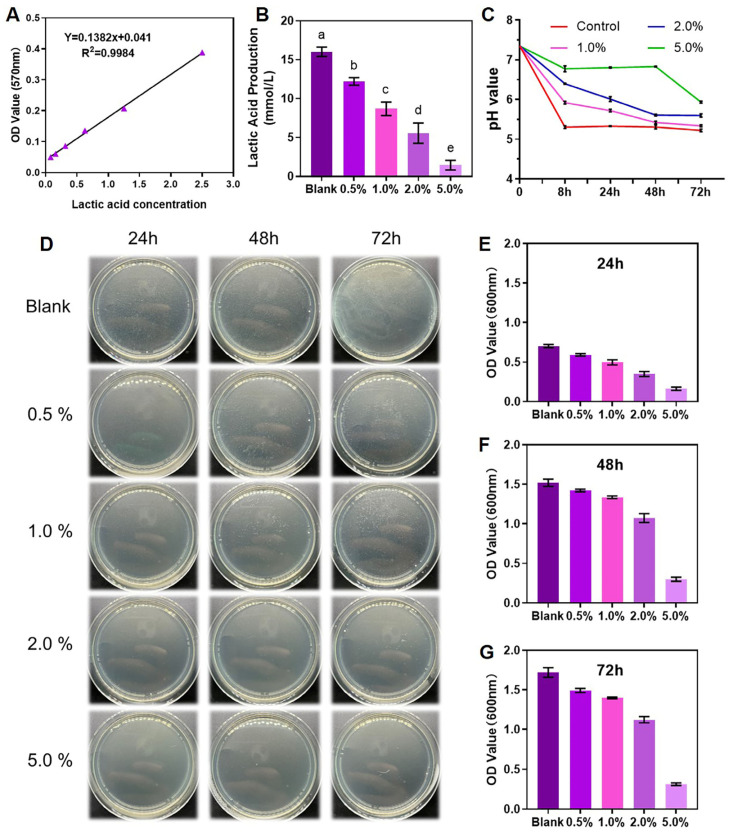
Figure 3.
Antibacterial properties of the novel elastomeric ligatures. (A) The standard curve of lactic acid production. (B) The lactic acid production of Streptococcus mutans biofilms in 24 h. (C) Changes in the pH of the microenvironment after 8 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h of culturing Streptococcus mutans. (D) Colony-forming unit counts of biofilms at 24, 48, and 72 h. (E–G) Spectrophotometer counting of biofilms at 24, 48, and 72 h. The 5% DMAHDM group exhibited optimal antibacterial efficacy, significantly suppressing the lactic acid production and the proliferation of biofilm microorganisms (p < 0.05). The data are represented as Mean ± SD (n ≥ 3). The different letters indicated significant differences (p < 0.05).