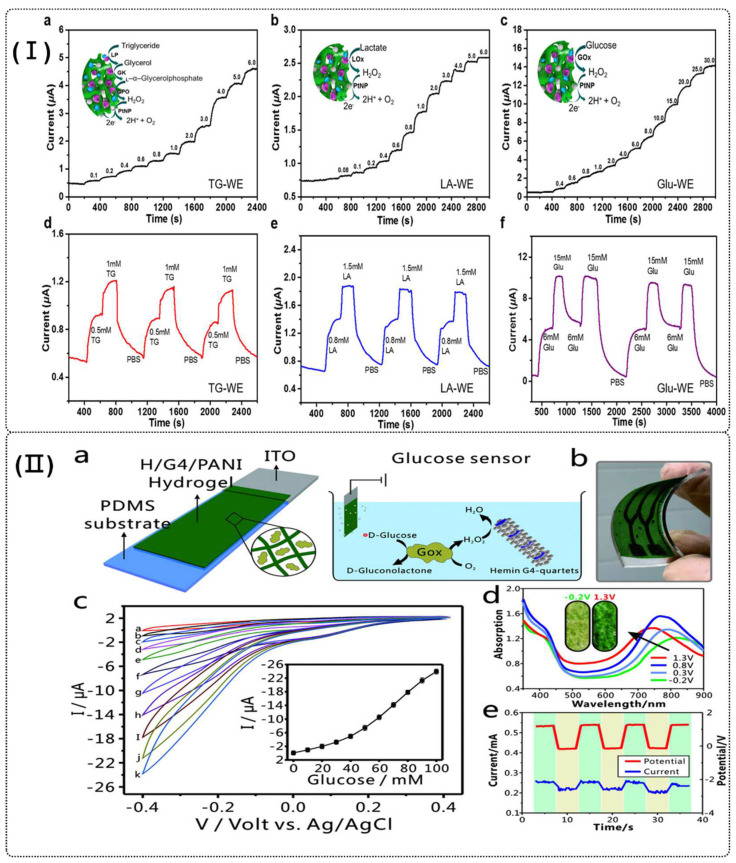
Figure 7.
(I) Instant current–time response curves, repeatability, and sensing mechanisms of the corresponding metabolites of printed biosensors when metabolite solutions with different concentrations were pumped into the channel in an alternating manner (flow velocity: 200 μL/min). (a,d) TG-WE detects triglyceride. (b,e) LA-WE detects lactate. (c,f) Glu-WE detects glucose. The insets in (a–c) show the schematic sensing mechanisms of the corresponding metabolites by the PAni hydrogel/PtNP enzymatic biosensors [78]. (II) (a) Scheme of the glucose sensor based on GOx-loaded H/G4–PANI hydrogel for the detection of glucose. (b) The image of the glucose sensor. (c) Cyclic voltammograms of glucose sensor in the presence of different concentrations of glucose. Inset indicates the linear correlation of cathodic peak current with the concentration of glucose. (d) UV–Vis absorption spectra of the H/G4–PANI hydrogel film measured in HCl solution. Inset are the photographic images of the H/G4–PANI hydrogel film at different applied potentials. (e) Potential and chronoamperometry curves of the H/G4–PANI hydrogel film [130].