FIGURE 1.
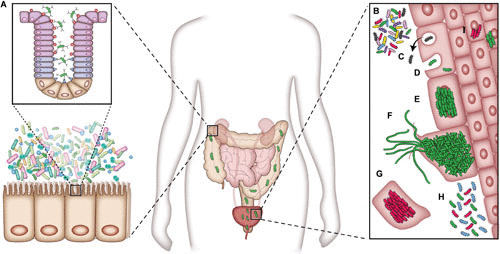
UPEC pathogenesis. (A) UPEC is housed in a reservoir in the gastrointestinal system. The bacteria are able to colonize the urinary tract from this reservoir. (B) Bacteria are able to adhere to and invade the bladder epithelial cells. (C) Bacterial cells can be evicted from the host cell in response. Bacterial cells can also enter the cytoplasm (D) and initiate IBC formation (E). (F) UPEC can, upon fluxing out of the host cells, filament and reinfect other urothelial cells. (G) To counteract intracellular pathogens, the host can initiate a program of host cell exfoliation. (H) Chronic cystitis in mice can occur with persistent high titers of bacteriuria. (I) QIRs can be established, in mice with resolved infections, in layers below superficial urothelial cells. Image and caption are adapted from reference 31.
