Abstract
A theoretical model for the expression of enzymic activity in reverse micelles previously developed [Bru. Sánchez-Ferrer & García-Carmona (1989) Biochem. J. 259, 355-361] was extended in the present work. The substrate concentration in each reverse-micelle phase (free water, bound water and surfactant apolar tails) and the organic solvent was expressed as a function of the total substrate concentration, taking into account its partition coefficients, that is, partitioning of the substrate in a multiphasic system. In each phase the enzyme expresses a catalytic constant and a Km. Thus the whole reaction rate is the addition of the particular rates expressed in each domain. This model was compared with that developed for a biphasic system [Levashov, Klyachko, Pantin, Khmelnitski & Martinek (1980) Bioorg. Khim. 6, 929-943] by fitting the experimental results obtained with mushroom tyrosinase (working on both 4-t-butylcatechol and 4-methylcatechol) to the two models. The parameters which characterize reverse micelles, omega 0 (water/surfactant molar ratio) and theta (fraction of water) were investigated. The omega 0 profile was shown to be hyperbolic for both substrates. Activity towards 4-t-butylcatechol decreases as theta increases, this observation being attributable to a dilution of the substrate. A Km of 7.8 M for 4-t-butylcatechol could be calculated on the basis of the biphasic model, whereas it was 13.5 mM when calculating on the basis of our model. A new parameter, rho (= [substrate]/theta), was defined to characterize those substrates that mainly solubilize in the reverse micelle ('micellar substrates').
Full text
PDF


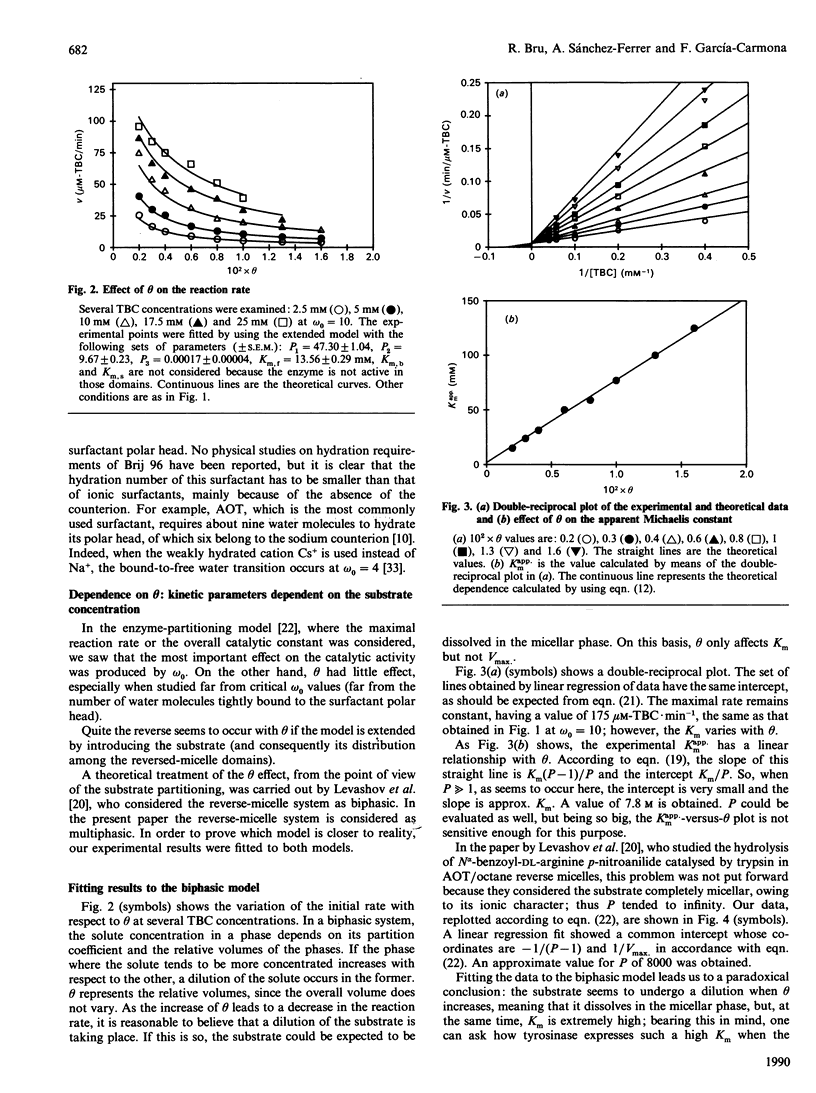
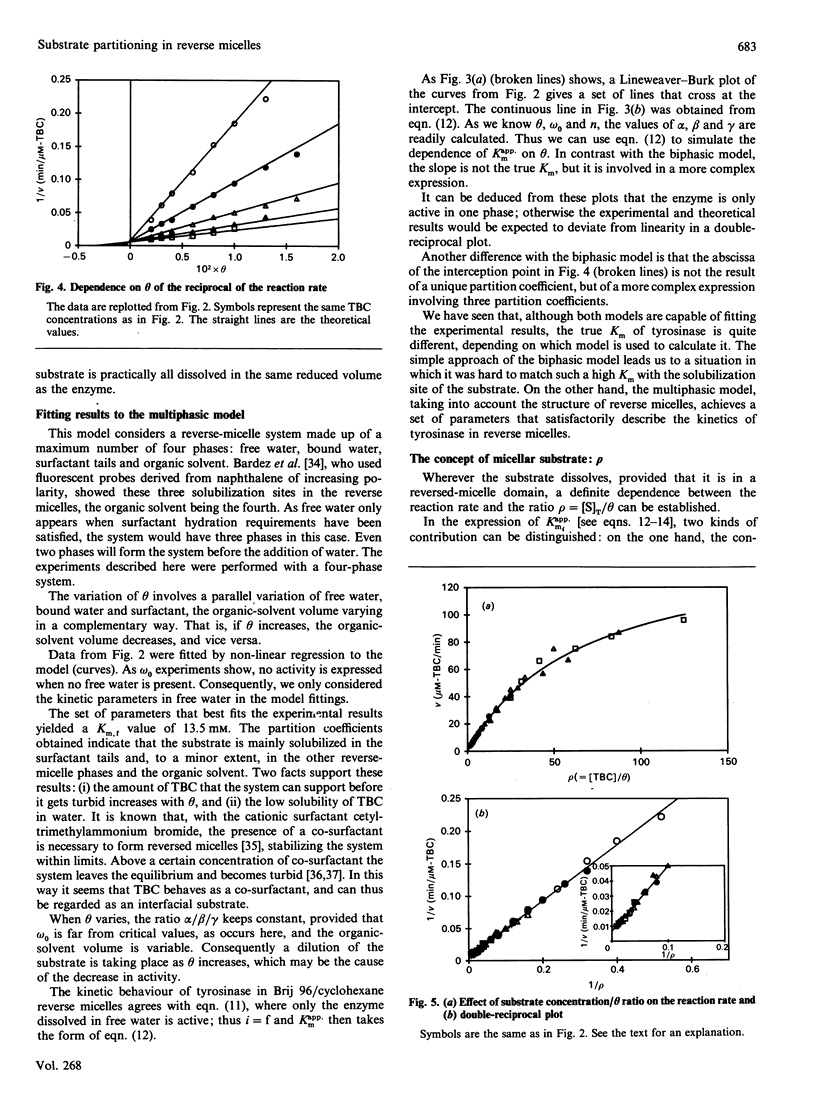

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bru R., Sánchez-Ferrer A., Garcia-Carmona F. A theoretical study on the expression of enzymic activity in reverse micelles. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):355–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2590355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabanes J., García-Cánovas F., Lozano J. A., García-Carmona F. A kinetic study of the melanization pathway between L-tyrosine and dopachrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 20;923(2):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker M., Hilhorst R., Laane C. Isolating enzymes by reversed micelles. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 1;178(2):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90628-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilhorst R., Spruijt R., Laane C., Veeger C. Rules for the regulation of enzyme activity in reserved micelles as illustrated by the conversion of apolar steroids by 20 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):459–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez M., Garcia-Carmona F., Garcia-Canovas F., Iborra J. L., Lozano J. A., Martinez F. Chemical intermediates in dopamine oxidation by tyrosinase, and kinetic studies of the process. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Dec;235(2):438–448. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi P. L., Giomini M., Pileni M. P., Robinson B. H. Reverse micelles as hosts for proteins and small molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):209–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luisi P. L., Magid L. J. Solubilization of enzymes and nucleic acids in hydrocarbon micellar solutions. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(4):409–474. doi: 10.3109/10409238609081999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malakhova E. A., Kurganov B. I., Levashov A. V., Berezin I. V., Martinek K. Novyi podkhod k izucheniiu fermentativnykh reaktsii s uchastiem nerastvorimykh v vode substratov. Pankreaticheskaia lipaza, vkliuchennaia v obrashchennye mitselly poverkhnostno-aktivnogo veshchestva v organicheskom rastvoritele. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1983;270(2):474–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinek K., Khmel'nitskii Iu L., Levashov A. V., Berezin I. V. Substratnaia spetsifichnost' alkogol'degidrogenazy v kolloidnom rastvore vody v organicheskom rastvoritele. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1982;263(3):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinek K., Kliachko N. L., Levashov A. V., Berezin I. V. Mitselliarnaia énzimologiia. Kataliticheskaia aktivnost' peroksidazy v kolloidnom rastvore vody v organicheskom rastvoritele. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1983;269(2):491–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinek K., Levashov A. V., Klyachko N. L., Pantin V. I., Berezin I. V. The principles of enzyme stabilization. VI. Catalysis by water-soluble enzymes entrapped into reversed micelles of surfactants in organic solvents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 15;657(1):277–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinek K., Levashov A. V., Klyachko N., Khmelnitski Y. L., Berezin I. V. Micellar enzymology. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 17;155(3):453–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walde P., Peng Q., Fadnavis N. W., Battistel E., Luisi P. L. Structure and activity of trypsin in reverse micelles. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 15;173(2):401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


