FIGURE 9.
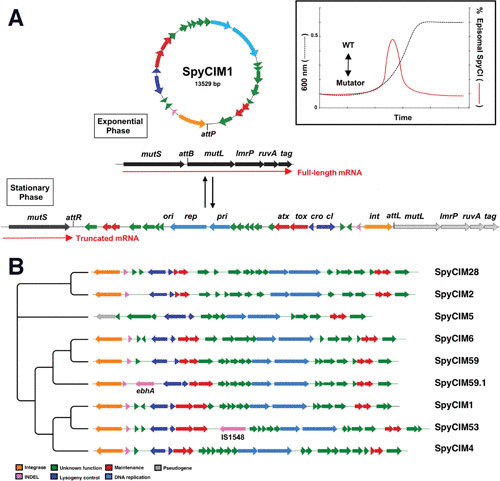
(A) SpyCIM1 regulation of the MMR operon through dynamic site-specific excision and integration. The MMR operon of S. pyogenes groups the genes encoding DNA MMR (mutS and mutL), multidrug efflux (lmrP), Holliday-junction resolvase (ruvA), and base excision repair glycosylase (tag). The orientation of this chromosomal region is shown here from the lagging strand to emphasize the MMR operon transcription. During exponential phase, SpyCIM1 excises from the chromosome, circularizes, and replicates as an episome, restoring transcription of the entire DNA MMR operon (WT). Excision and mobilization occur early in logarithmic growth in response to as yet unknown cellular signals (insert; adapted from Scott et al. [53]). As logarithmic growth continues, SpyCIM1 reintegrates into mutL at attB, and by the time the culture reaches the stationary phase, the integration process has completed, again blocking transcription of the MMR operon. WT, wild-type phenotype associated with unimpeded expression of the MMR operon. Reproduced from Frontiers in Microbiology (52) under the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0). (B) The phylogenetic tree of the SpyCI DNA sequences is presented. The tree was created with TreeGraph 2 (111) using previously analyzed data (52).
