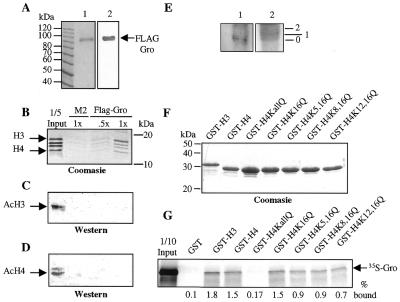
Figure 3.
Gro interacts preferentially with hypoacetylated forms of histones. (A) SDS–PAGE gels of baculovirus produced and purified FLAG-Gro. Lane 1, Coomasie blue stained gel; lane 2, anti-FLAG western blot. The molecular masses in kDa of protein size markers are indicated. (B) Purified Drosophila histones were incubated with either 30 µl (.5x) or 60 µl (1x) of FLAG-Gro immobilized on agarose–M2 beads or with 60 µl (1x) of agarose–M2 beads alone. After incubation, one-third of the bound histones was analyzed by Coomasie blue staining. (C and D) Western blot analyses of the input and retained fractions from the affinity chromatography experiment in (B). Two-thirds of the retained histones were analyzed with anti-acetylated H3 (C) or anti-acetylated H4 (D) polyclonal antibodies. (E) Far western analysis of histone H3 resolved by TAU electrophoresis and probed with FLAG-Gro. Lane 1, far western analysis; lane 2, Coomasie blue staining. 0, 1 and 2 indicate positions of unacetylated, singly-acetylated, and doubly-acetylated species, respectively. (F) Wild-type GST–H3 and either wild-type or the indicated single or double point mutant forms of GST–H4 were produced and purified from E.coli and visualized by Coomasie blue staining. Approximately equal amounts of proteins were used for the interaction assays. (G) Autoradiogram of a GST-pulldown assay with 35S-Gro and the indicated GST–histone tail variants.