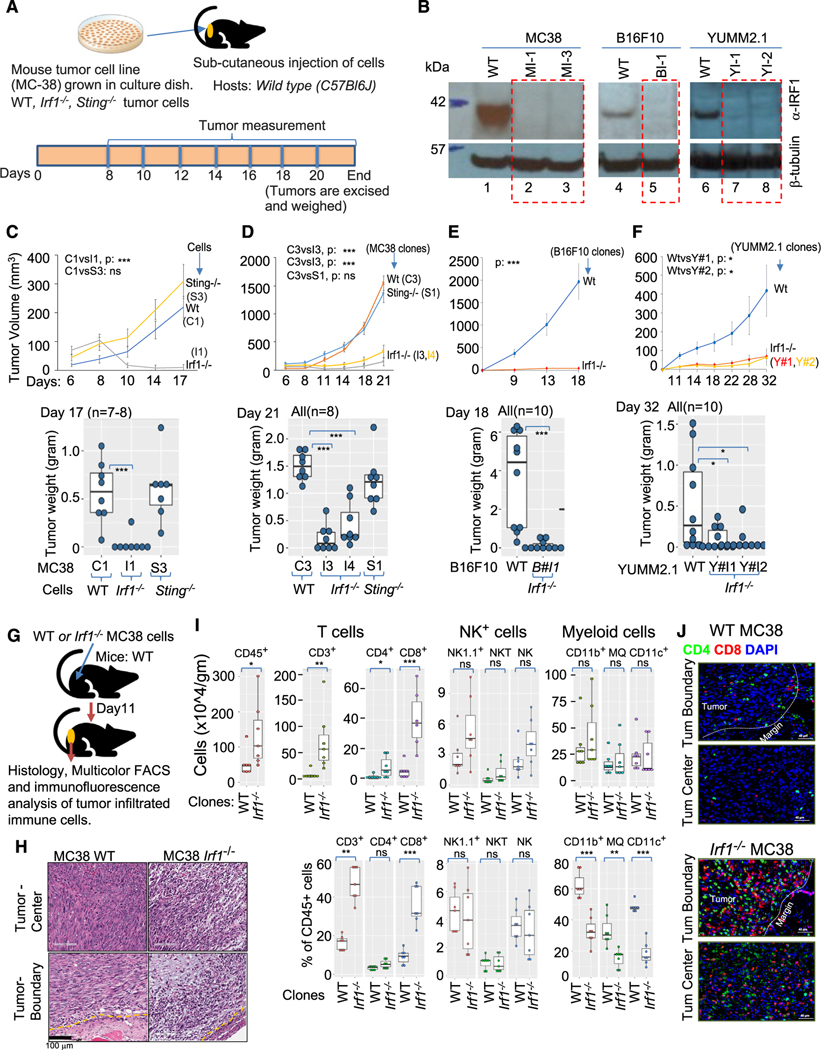
Figure 1. Increased infiltration of adaptive immune cells is associated with growth impairment of immunogenic Irf1−/− tumor.
(A) Schematic representation of syngeneic tumor model.
(B) Immunoblot using anti-IRF1 antibody (top panel) anti-β-tubulin (bottom panel) loading control showing loss of IRF1 expression in various CRISPR-Cas937 mutant tumor clones.
(C) Upper panel shows growth kinetics of a representative experiment of WT (C1), Irf1−/− (I1), and Sting−/− (S3) MC38 clones in wild-type (C57BL/6J) hosts. Lower panel represents weight of tumors at termination of experiment in upper panel.
(D) Upper panel shows tumor growth kinetics (average tumor volume) of additional WT (C3), Sting−/− (S1), and Irf1−/− (I3 and I4) MC38 clones in wild-type (C57BL/6J) hosts. Lower panel shows weight of tumors from panel above on day 21.
(E) Upper panel shows growth kinetics of one each of WT and Irf1−/− B16F10 clones. Lower panel represents weight of tumors on day 18 from the experiment shown above.
(F) Upper panel shows growth kinetics of one WT and two Irf1−/− YUMM2.1 clones. Lower panel represents weight of tumors on day 32 from the experiment above. For (C)–(F), p values were determined. Error bars represent mean ± standard error. *p ≤ 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 by Mann-Whitney U/Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Student’s paired t test as appropriate.
(G) Schematic representation of experimental approach for (H)–(J).
(H) Histology of tumor center and tumor boundary from WT (top left, bottom left) and Irf1−/− (top right, bottom right) from WT (bottom left) and Irf1−/− (bottom right) MC38 tumors grown in WT mice.
(I) Flow cytometry analysis of tumors for CD8+ and NK cells in the Irf1−/− MC38 tumors from WT (C57BL/6J) mice. Upper and lower panels represent immune cells/gram tumors and percent tumor CD45+ cells, respectively. p values were determined by a Mann-Whitney U/Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Student’s paired t test as appropriate. *p ≤ 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
(J) Representative immunofluorescence photomicrographs of tumor boundary (top panel) and tumor center (bottom panel) of WT (upper) and Irf1−/− (lower) MC38 tumors in WT mice.