Abstract
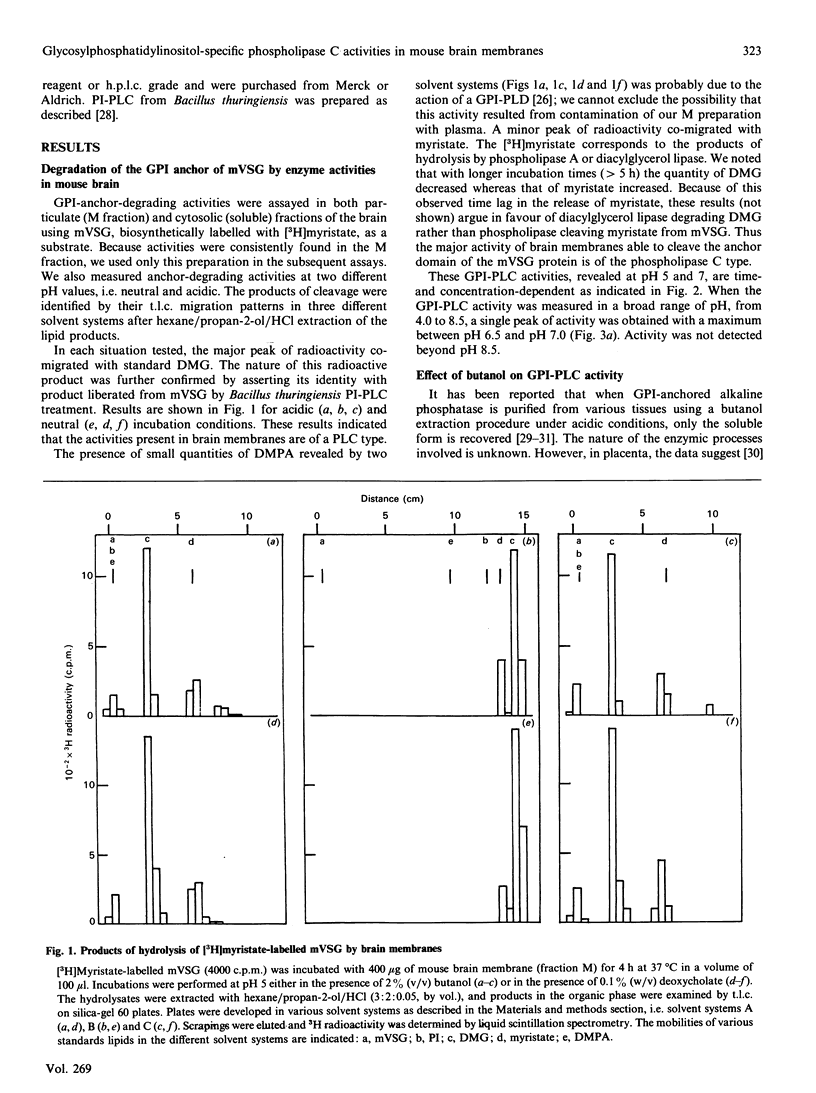
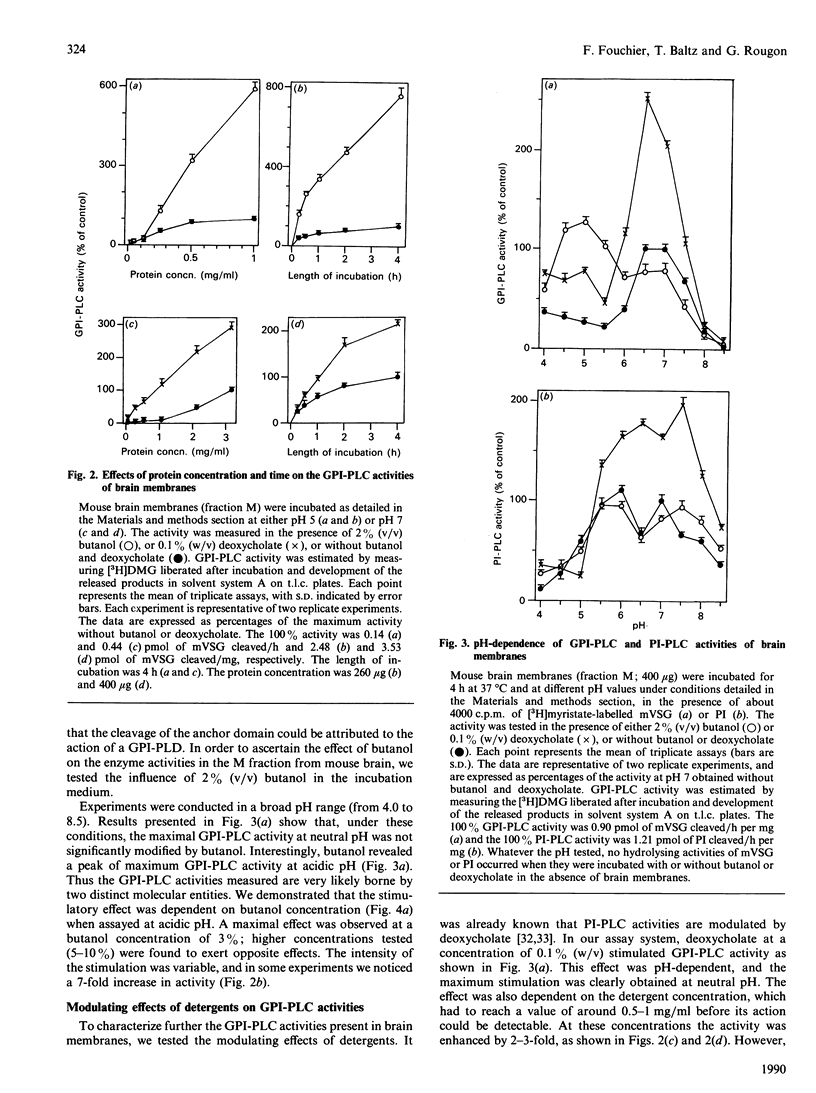
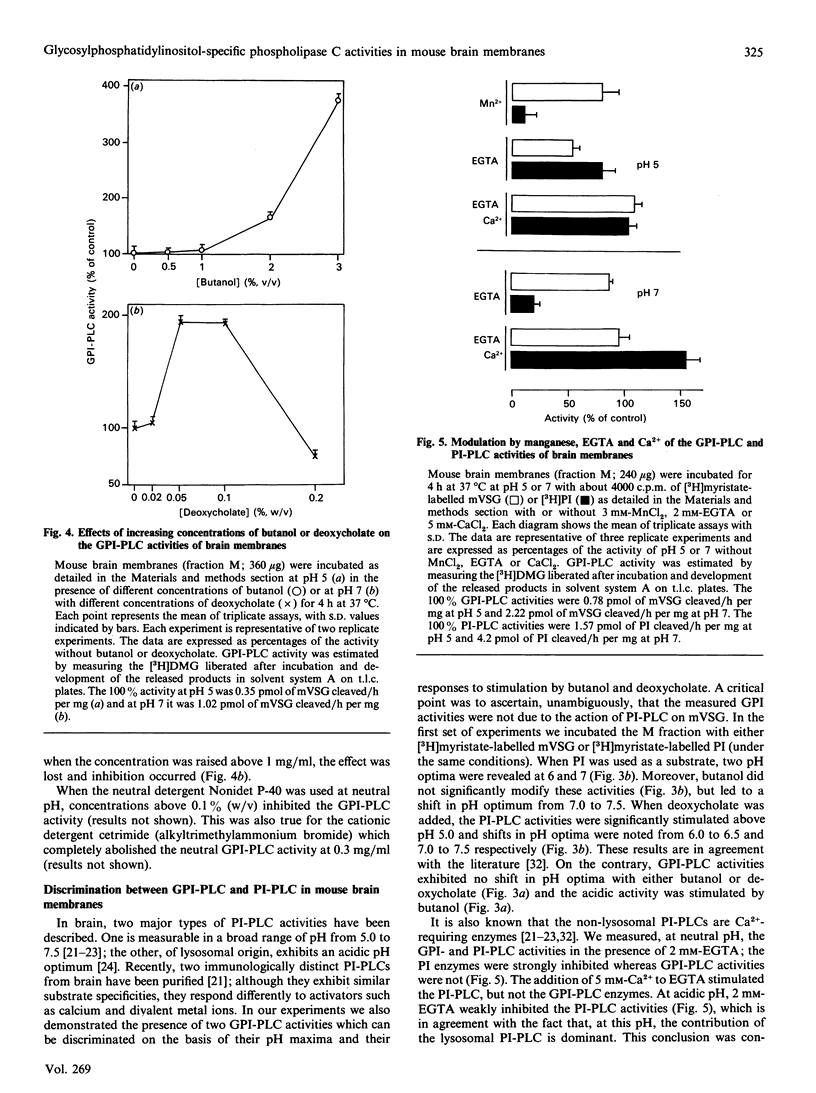
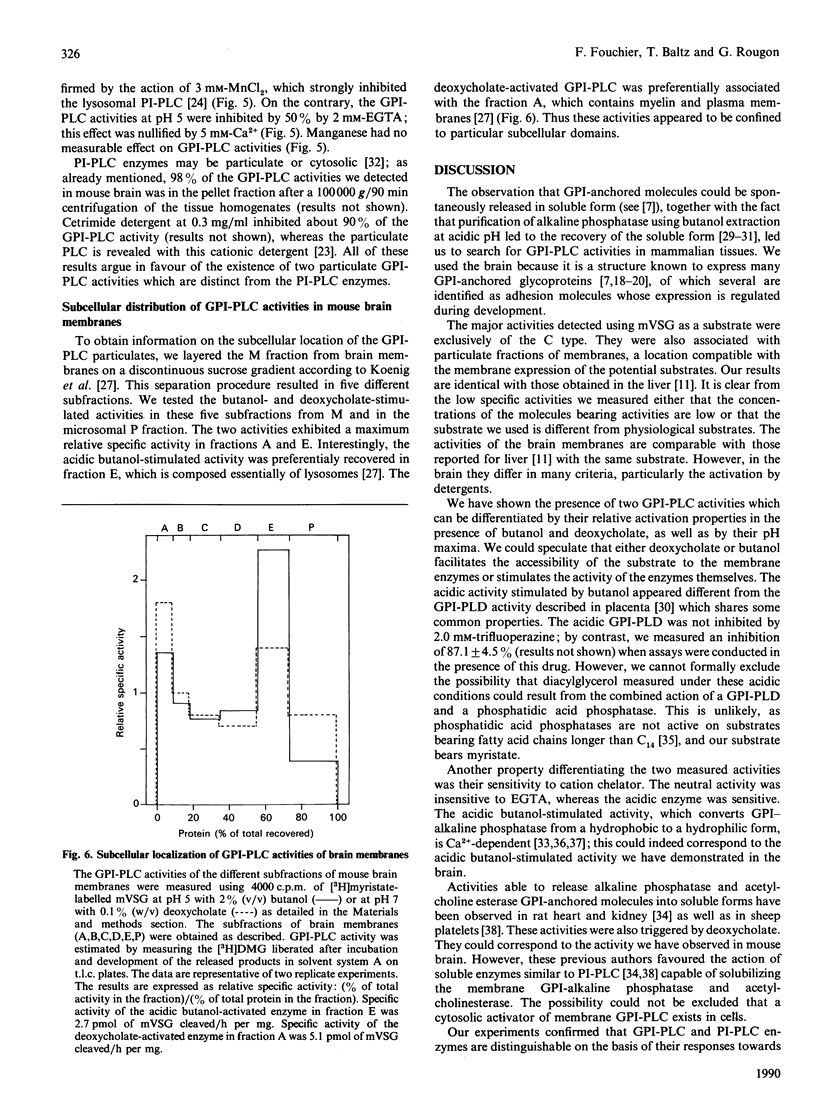
Using the membrane form of variant surface glycoprotein from Trypanosoma equiperdum labelled with [3H]myristate as a substrate, we identified two glycosylphosphatidylinositol phospholipase C enzymic activities in mouse brain. These activities were associated with particulate membrane fractions. They were characterized by their pH activity maxima and sensitivity to activators and ion chelators. One of the activities was maximal at acidic pH, stimulated by butanol, sensitive to cation chelator and insensitive to manganese. The activity of the other was maximal at neutral pH, stimulated by the detergent deoxycholate and independent of the presence of cation chelator or calcium. On membrane subfractionation, the acidic butanol-stimulated activity was found mainly associated with the lysosomal compartment, whereas the neutral deoxycholate-stimulated activity sediments with the myelin and plasma membrane compartment. These activities could be differentiated from particulate phosphatidylinositol phospholipases C, whose acidic lysosomal form is sensitive to manganese and insensitive to cation chelator or butanol, whereas the deoxycholate-activated enzymes are Ca2(+)-dependent.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almqvist P., Carlsson S. R. Characterization of a hydrophilic form of Thy-1 purified from human cerebrospinal fluid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12709–12715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergers M., Lendi S., Mier P. D. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phospholipase C activity in particulate preparations from rat brain. Lipids. 1989 Jan;24(1):13–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02535258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow R., Overath P. Purification and characterization of the membrane-form variant surface glycoprotein hydrolase of Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11918–11923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Hereld D., Shak S., Krakow J., Englund P. T., Nussenzweig V. A glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D in human serum. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2443973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Myristylation of the membrane form of a Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3011–3015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouchier F., Bastiani P., Baltz T., Aunis D., Rougon G. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol is involved in the membrane attachment of proteins in granules of chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):103–108. doi: 10.1042/bj2560103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Duszenko M., Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Purification and characterization of a novel glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15767–15771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Soliz N. M., Saltiel A. R. Purification of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase C from liver plasma membranes: a possible target of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennarini G., Rougon G., Vitiello F., Corsi P., Di Benedetta C., Goridis C. Identification and cDNA cloning of a new member of the L2/HNK-1 family of neural surface glycoproteins. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Jan;22(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490220102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawrylak K., Stinson R. A. The solubilization of tetrameric alkaline phosphatase from human liver and its conversion into various forms by phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C or proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14368–14373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He H. T., Finne J., Goridis C. Biosynthesis, membrane association, and release of N-CAM-120, a phosphatidylinositol-linked form of the neural cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2489–2500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Bangs J. D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A phospholipase C from Trypanosoma brucei which selectively cleaves the glycolipid on the variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13813–13819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara M., Fedarko N. S., Conrad H. E. Involvement of phosphatidylinositol and insulin in the coordinate regulation of proteoheparan sulfate metabolism and hepatocyte growth. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4708–4716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG H., GAINES D., MCDONALD T., GRAY R., SCOTT J. STUDIES OF BRAIN LYSOSOMES. I. SUBCELLULAR DISTRIBUTION OF FIVE ACID HYDROLASES, SUCCINATE DEHYDROGENASE AND GANGLIOSIDES IN RAT BRAIN. J Neurochem. 1964 Oct;11:729–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami T., Miki A., Ikehara Y. Electrophoretic characterization of hepatic alkaline phosphatase released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. A comparison with liver membrane and serum-soluble forms. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):183–189. doi: 10.1042/bj2270183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel D., Beattie M. The major protein of pancreatic zymogen granule membranes (GP-2) is anchored via covalent bonds to phosphatidylinositol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):818–823. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol: a versatile anchor for cell surface proteins. FASEB J. 1989 Mar;3(5):1600–1608. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.5.2522071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Prasad A. R. A phospholipase D specific for the phosphatidylinositol anchor of cell-surface proteins is abundant in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Zilversmit D. B. Role of phosphatidylinositol in attachment of alkaline phosphatase to membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):3913–3918. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar R., Balasubramanian A. S. The solubilization of platelet membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase and aryl acylamidase by exogenous or endogenous phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 1;34(23):4109–4115. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. S., Low M. G. Conversion of human placental alkaline phosphatase from a high Mr form to a low Mr form during butanol extraction. An investigation of the role of endogenous phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2400519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki A., Kominami T., Ikehara Y. pH-dependent conversion of liver-membranous alkaline phosphatase to a serum-soluble form by n-butanol extraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki A., Tanaka Y., Ogata S., Ikehara Y. Selective preparation and characterization of membranous and soluble forms of alkaline phosphatase from rat tissues. A comparison with the serum enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):41–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Weiss S. J., Van De Walle C. M., Haddas R. A. Is phosphatidic acid a calcium ionophore under neurohumoral control? Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):345–347. doi: 10.1038/284345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Rosen O. M. Purification of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12526–12532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J. Two different biosynthetic pathways for the secretion of Qa region-associated class I antigens by mouse lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):527–531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick B., Hübscher G. Metabolism of phospholipids. X. Partial purification and properties of a soluble phosphatidate phosphohydrolase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):397–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Conrad H. E. Formation of anhydrosugars in the chemical depolymerization of heparin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3932–3942. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D. Minireview. Phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipases C. Life Sci. 1982 Apr 19;30(16):1323–1335. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Borchelt D. R., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi R., Asahi Y., Ikezawa H. Purification and properties of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 14;619(1):48–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida M. L., Turner M. J., Stambuk B. B., Schenkman S. Identification of an acid-lipase in human serum which is capable of solubilizing glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):476–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


