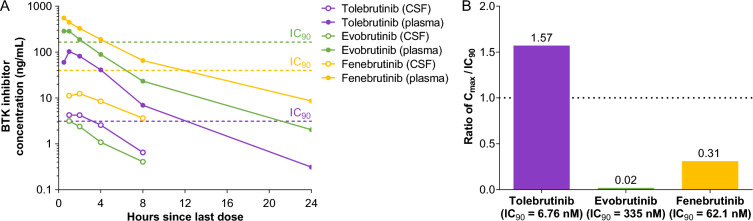
Fig. 3.
CNS exposure of three BTK inhibitors in nonhuman primates. Three healthy male animals were used in a crossover study conducted by a third-party vendor (Biomere, Worcester, MA). On days 1–4, animals received a single daily oral dose of one of three test articles at 3 or 10 mg/kg that were supplied using a blinding code such that the identity of the substances was unknown to the vendor. The dose was delivered by oral gavage in a volume of 5 mL/kg. Following a 7-day washout period, the same three animals received a single daily oral dose of a second test article at 3 or 10 mg/kg. This sequence was repeated a third time for the final test article. Data presented for the 10 mg/kg dose. A The plasma (filled symbols) and CSF (open symbols) concentrations of test article (indicated in the legend) are plotted as a function of time post-administration. The dashed horizontal lines represent the IC90 value for each test article as described above (see Table 2). Data represent the mean values from the three animals. B The maximal CSF exposure observed is plotted relative to the in vitro IC90 for each test article to estimate the extent to which the test article achieved bioactive exposures. At the dose of 10 mg/kg, only tolebrutinib exceeded the estimated IC90 value (1.57-fold) while evobrutinib (0.02-fold) and fenebrutinib (0.31-fold) failed to reach their respective IC90 values