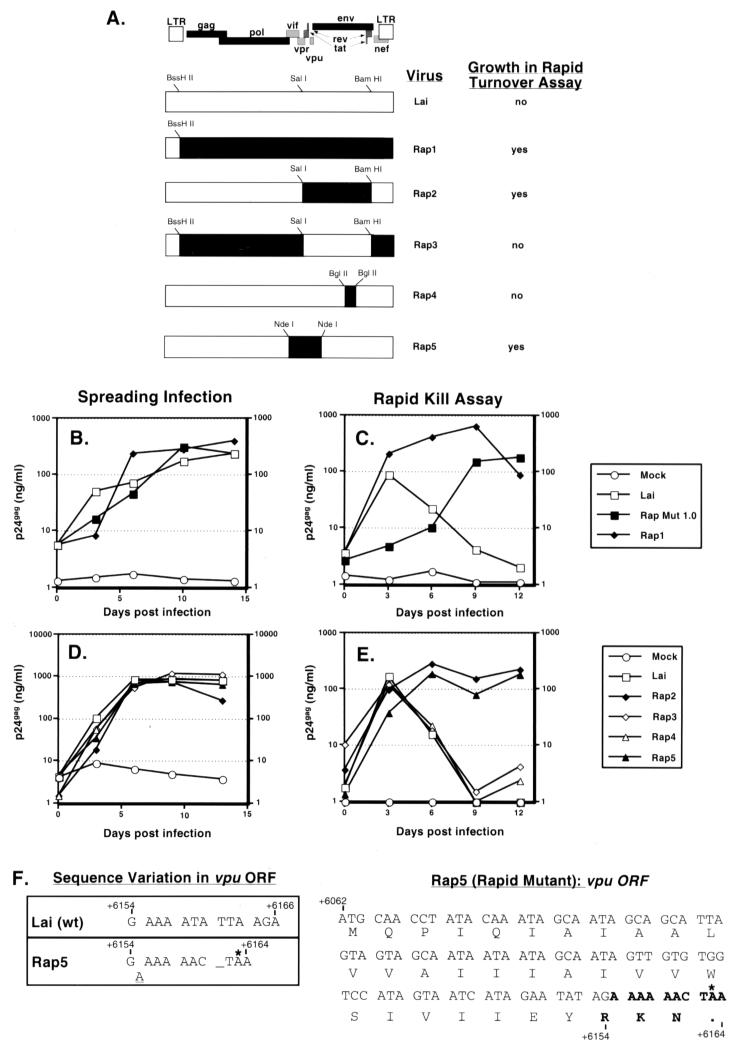
FIG. 2.
Characterization of mutations necessary for survival of the selected virus in the rapid-turnover assay. (A) Full-length HIVs with the indicated genomic composition were derived as described in Materials and Methods. Restriction sites used for cloning are indicated on each recombinant plasmid. Solid regions indicate sequences derived from the rapid mutant, while open boxes indicate sequences derived from Lai. The phenotypes of each of the chimeras in the rapid-turnover assay are indicated. Jurkat cells (106) were infected with the viral chimeras at an MOI of 0.03. (B to E) Cultures were subjected to the rapid-turnover assay protocol (C and E), as described in Materials and Methods, or infections were allowed to progress in the absence of mitomycin C (B and D). Cell-free culture supernatants were assayed for p24gag content by ELISA. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. (F) The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the wild-type (wt) and mutant vpu ORFs are shown and numbered according to the HXB2R clone sequence. The insertion of the A nucleotide in the mutant vpu ORF is indicated by a dash, and the termination codon indicated by an asterisk.