Abstract
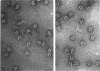
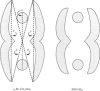
alpha 2-Macroglobulin-methylamine (alpha 2M-CH3NH2) was digested with papain at pH 5.0. The major 600 kDa fragment was purified by molecular-exclusion chromatography. In a non-denaturing gel-electrophoresis system, the 600 kDa fragment migrated in a single band at a rate that was comparable with that for the untreated alpha 2M-CH3NH2. The elution volume of the 600 kDa fragment on Superose-6 was slightly increased. In primary cultures of rat hepatocytes, cellular uptake of 125I-alpha 2M-CH3NH2 was not affected by the 600 kDa fragment, confirming the results of other investigators. The 600 kDa fragment was negatively stained with uranyl formate and analysed by transmission electron microscopy. The major structural characteristics of the parent protein (alpha 2M-CH3NH2) remained intact. The most common image included prominent lateral walls and two centrally located regions of stain exclusion termed 'paddle structures'. The distance between the paddle structures was equivalent in alpha 2M-CH3NH2 and the 600 kDa fragment [approximately 13.5 nm (135 A)]. By contrast, the lateral walls in the 600 kDa fragment were decreased in length by approximately 0.37 nm (37 A) (19%). It is proposed that the 600 kDa structure retains the 'hollow cylinder' shape of alpha 2M-CH3NH2. The structure of the cylinder is formed by the lateral walls and four paddle structures (only two are imaged, owing to overlapping). The paddle structures in the 600 kDa fragment are intact and relatively closer to the apices of the molecule, owing to the decrease in lateral wall length. Since the alpha 2M receptor-binding sites are removed by papain digestion, the studies presented here support the location of the receptor-binding sites near the apices of the lateral walls.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boisset N., Taveau J. C., Pochon F., Tardieu A., Barray M., Lamy J. N., Delain E. Image processing of proteinase- and methylamine-transformed human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Localization of the proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):12046–12052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretaudiere J. P., Tapon-Bretaudiere J., Stoops J. K. Structure of native alpha 2-macroglobulin and its transformation to the protease bound form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1437–1441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delain E., Barray M., Tapon-Bretaudiere J., Pochon F., Marynen P., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H., Van Leuven F. The molecular organization of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. An immunoelectron microscopic study with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2981–2989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Allietta M. M., Pizzo S. V., Castellino F. J., Tillack T. W. Electron microscopic identification of exposed plasmin epitopes in alpha 2-macroglobulin-plasmin complex using monoclonal antibody-colloidal gold adducts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10903–10906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Braud L. L., Geary W. A., VandenBerg S. R. Plasminogen binding to rat hepatocytes in primary culture and to thin slices of rat liver. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):729–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Figler N. L. Electron microscopy studies of alpha 2-macroglobulin conformational intermediates obtained by derivatization with cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum (II). J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9565–9570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Reynolds J. A., Pizzo S. V. Physical properties of human alpha 2-macroglobulin following reaction with methylamine and trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 10;705(3):306–314. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Swaim M. W., Massey M. F., Pizzo S. V. cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum (II) as a selective modifier of the oxidation-sensitive reactive-center methionine in alpha 1-antitrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Physical and chemical properties of human plasma alpha2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1730027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin-enzyme interactions. Evidence for proteolytic modification of the subunit chain structure. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):508–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of two electrophoretic "fast" forms of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8134–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Ray F. A., Keogh E. A. Recognition of nucleophile-treated alpha 2-macroglobulin by the alveolar macrophage alpha-macroglobulin . protease complex receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7705–7707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurecki T., Kress L. F., Laskowski M., Sr Purification of human plasma alpha 2 macroglobulin and alpha 1 proteinase inhibitor using zinc chelate chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):415–420. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan T. Electrophoresis buffers for polyacrylamide gels at various pH. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):94–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishigai M., Osada T., Ikai A. Structural changes in alpha-2- and ovomacroglobulins studied by gel chromatography and electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 4;831(2):236–241. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Strickland D. K., Enghild J. J., Pizzo S. V. Evidence that the platinum-reactive methionyl residue of the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor recognition site is not in the carboxyl-terminal receptor binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6715–6721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Gliemann J., Van Leuven F. Domain structure of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Characterization of a receptor-binding domain obtained by digestion with papain. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80857-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Stepanik T. M., Kristensen T., Wierzbicki D. M., Jones C. M., Lønblad P. B., Magnusson S., Petersen T. E. Primary structure of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. V. The complete structure. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8318–8327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapon-Bretaudiére J., Bros A., Couture-Tosi E., Delain E. Electron microscopy of the conformational changes of alpha 2-macroglobulin from human plasma. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):85–89. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van Den Berghe H. Demonstration of an alpha2-macroglobulin receptor in human fibroblasts, absent in tumor-derived cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5155–5160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Marynen P., Sottrup-Jensen L., Cassiman J. J., Van den Berghe H. The receptor-binding domain of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Isolation after limited proteolysis with a bacterial proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11369–11373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]