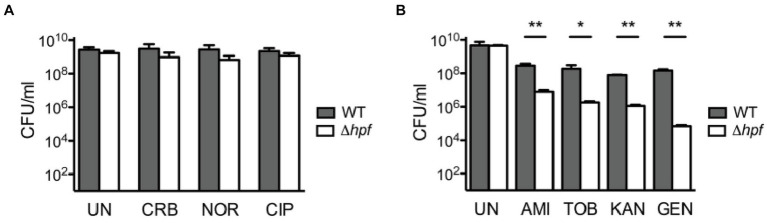
Figure 3.
Loss of hibernation factors in dormant bacteria potentiates aminoglycoside-mediated toxicity. (A) When cultures of wild-type (WT) and HPF-deficient Listeria monocytogenes are cultured for 72 h in stationary phase and then treated with various antibiotics, they show similar tolerance to the non-ribosome-targeting drugs carbenicillin (CRB), norfloxacin (NOR), and ciprofloxacin (CIP). UN indicates untreated cultures, and CFU stands for colony-forming units. (B) However, when stationary L. monocytogenes cultures are treated with aminoglycoside antibiotics, the HPF-deficient strain shows up to 3 orders of magnitude reduction in CFU compared to WT. Labels indicate the aminoglycoside antibiotics amikacin (AMI), tobramycin (TOB), kanamycin (KAN), and gentamicin (GEN) [this figure is reproduced from Ref (McKay and Portnoy, 2015) with permission from the American Association for Microbiology, license ID 1474012-1].