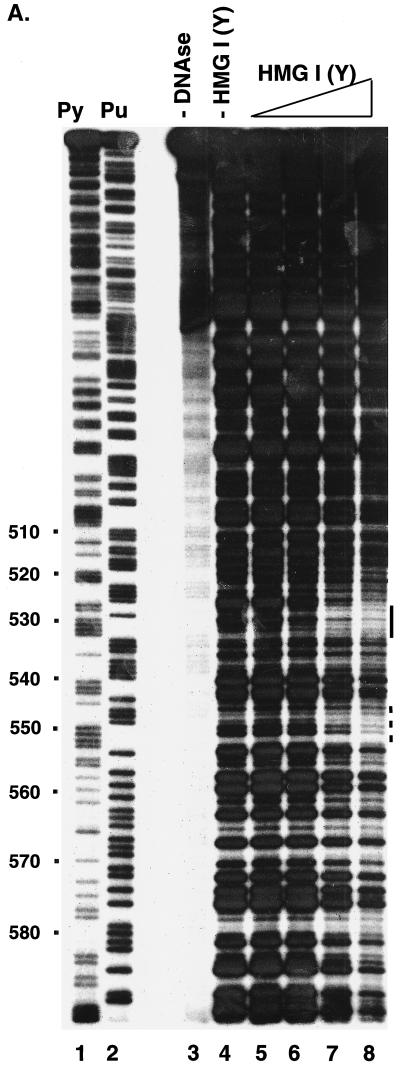
FIG. 4.
Analysis of binding of HMG I(Y) to the HIV-1 LTR. (A) Analysis by DNase I protection. A restriction fragment containing sequences 295 to 634 from the HIV-1 LTR was labeled with 32P on the 5′ end at an artificial NdeI site at the U5 edge of the LTR. Lanes: 1, cleavage at pyrimidine (Py) residues; 2, cleavage at purine (Pu) residues; 3, uncleaved DNA; 4 to 9, 0.1 U of DNase I per ml; 4, no added HMG I(Y); 5, 0.8 nM HMG I(Y); 6, 2 nM HMG I(Y); 7, 7 nM HMG I(Y); 8, 22 nM HMG I(Y). (B) Oligonucleotide probes used in the gel retardation assay. The wild-type probe corresponds to residues 404 to 467 of the HIV LTR (NL4-3, left LTR). MUT, mutant; sub, substitution. (C) Gel retardation analysis of binding to the wild-type probe by HMG I or HMG Y. The mobilities of the free probe and observed complexes are indicated beside the gel. Lanes 1 to 5 contained the following concentrations of HMG I: 1, 0.13 nM; 2, 0.8 nM; 3, 4 nM; 4, 20 nM; 5, 100 nM. Lanes 6 to 9 contained the following concentrations of HMG Y: 6, 0.8 nM; 7, 4 nM; 8, 20 nM; 9, 100 nM. (D) Rescue of binding to mutant sites by inosine substitution. The DNA substrates studied are marked above the gel. W.T., wild type. Lanes 1 to 7, no added protein; lanes 8 to 14, 1 nM HMG I.