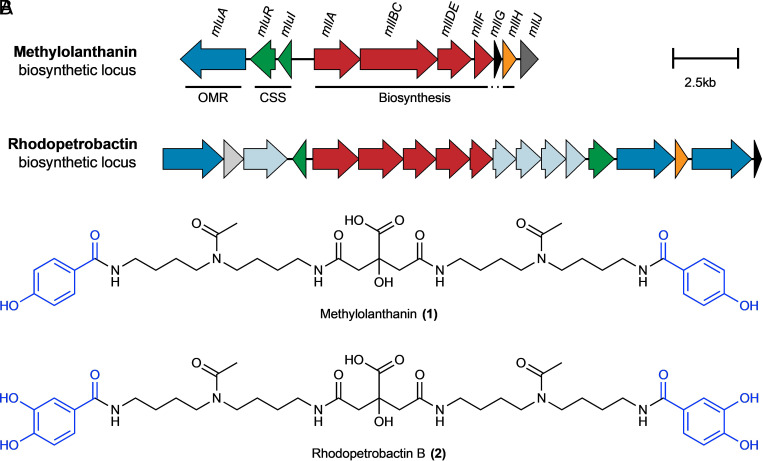
Fig. 2.
BGCs and chemical structures of methylolanthanin (1) and the related siderophore rhodopetrobactin (2). A, The methylolanthanin BGC from M. extorquens AM1 (mll/mlu, META1p4129-4138) and the rhodopetrobactin BGC from Rhodopseudomonas palustris TIE-1 (25). Homologous pathways between BGCs share the same color. Genes are drawn to scale. OMR, TonB-dependent outer membrane receptor; CSS, cell-surface signaling. Additional homologous clusters are presented in SI Appendix, Fig. S1. (B) Chemical structures of methylolanthanin (1) and rhodopetrobactin (2), which differ by the presence of 4-HB vs. 3,4-DHB, respectively (in blue).