Figure 1.
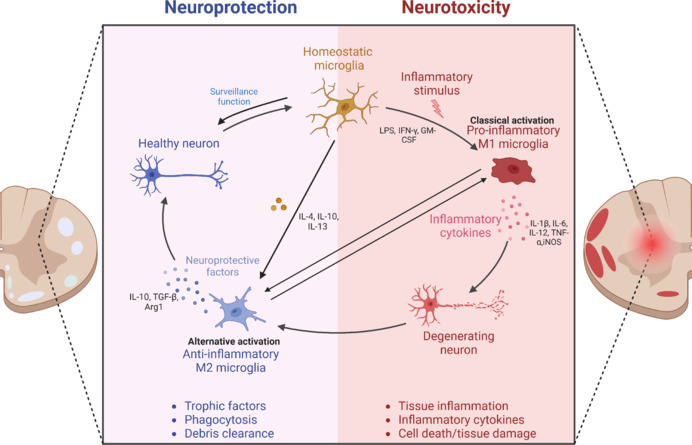
Effects of resting microglia and M1/M2 microglia on neurons.
Homeostatic microglia have a dynamic surveillance role in the CNS. Following spinal cord injury, microglia are activated into pro-inflammatory (M1) and anti-inflammatory (M2) microglia. The pro-inflammatory cytokines produced by M1 microglia, such as IL-1β, TNF-α, and iNOS, further aggravate damage, which could eventually cause the death of neurons, while the anti-inflammatory cytokines produced by M2 microglia, such as IL-10, can restore the damage and play a neuroprotective role. Created with BioRender.com. Arg1: Arginase-1; CNS: central nervous system; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-4: interleukin-4; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-10: interleukin-10; IL-12: interleukin-12; IL-13: interleukin-13; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; LPS: lipopolysaccharide; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β.
