Figure 7.
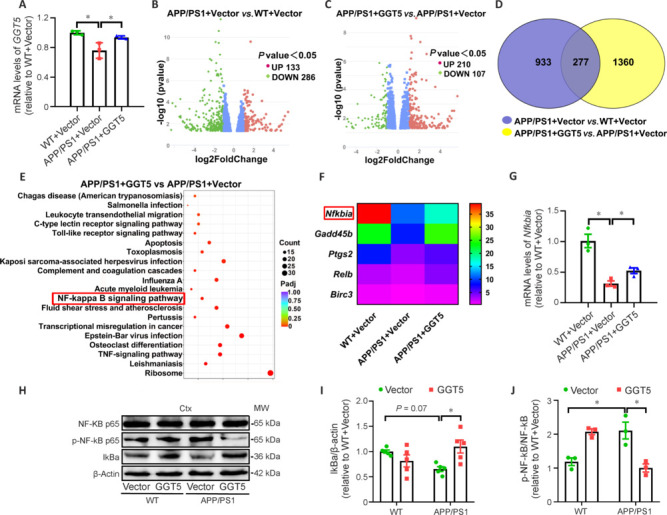
GGT5 overexpression in cerebrovascular endothelial cells suppresses the IκB/NF-κB signaling pathway.
(A) Histogram of GGT5 expression levels in the mouse cortex, as determined by qPCR (n = 3 per group). (B, C) Volcano plots showing differential gene expression based on mRNA-seq analysis in the mouse cortex in the APP/PS1 + Vector group vs. the WT + Vector group (B) and the APP/PS1 + GGT5 group vs. the APP/PS1 + Vector group (C). (D) Venn diagram showing that there were 277 differentially expressed genes in the mouse cortex in common between the WT + Vector group vs. the APP/PS1 + Vector group and the APP/PS1 + GGT5 group vs. the APP/PS1 + Vector group, as determined by mRNA-seq. (E) Pathway enrichment analysis of genes that were differentially expressed between the APP/PS1 + GGT5 group and the APP/PS1 + Vector group (the NF-κB pathway is highlighted). (F) Heatmap displaying the relative expression levels of differentially expressed genes involved in the NF-κB pathway. (G) Histogram of Nfkbia expression, as determined by qPCR, in the mouse cortex (n = 3 per group). (H–J) Representative western blots (each row is an image from a different blot) (H) and quantitative analysis of IκBα (I) and p-NF-κB/NF-κB (J) expression in the mouse cortex (n = 3–5 per group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). Birc3: Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 3; Ctx: cortex; Gadd45b: growth arrest and DNA damage inducible protein beta; GGT5: gamma-glutamyltransferase 5; IκBα: inhibitor-kappaBα; NFKbia: nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitorα; NF-κB: nuclear factor‐kappa B; p-NF-κB: phosphor nuclear factor‐kappa B; Ptgs2: prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2; qPCR: real-time polymerase chain reaction; Relb: recombinant v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; WT: wide type.
