Figure 1. The hair follicle forms a functioning barrier.
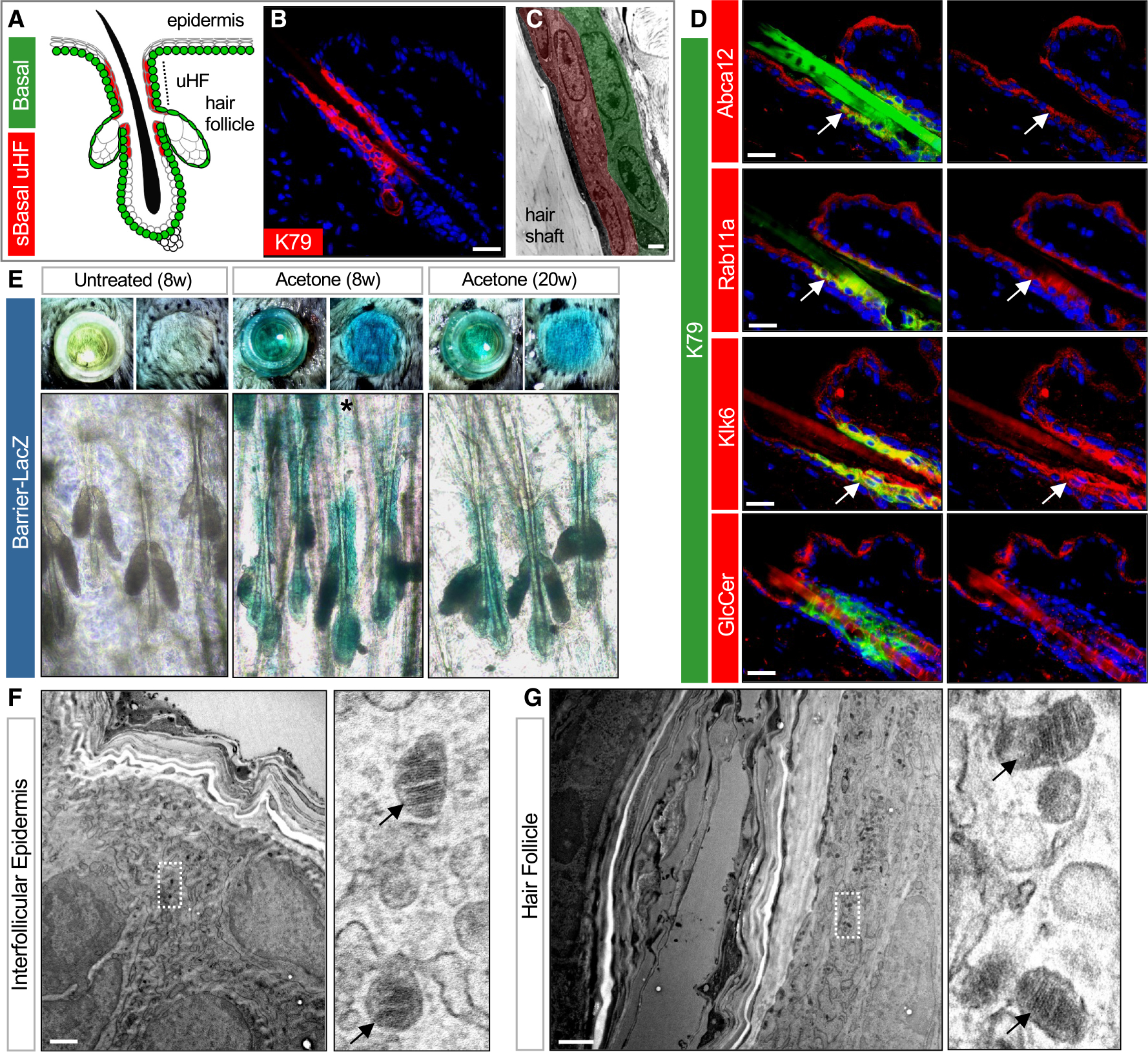
(A) Schematic of telogen hair follicle. Green, basal progenitors. Red, K79+ suprabasal (sBasal) cells in the upper hair follicle (uHF). Note that K79 is also expressed by sebocytes31 (not highlighted here).
(B) Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for K79 (red).
(C) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of uHF showing basal (green) and suprabasal (red) hair follicle epithelium and hair shaft.
(D) IHC for barrier-associated proteins (red) and K79 (green). Right images show single-channel views of barrier-associated protein expression. Arrows, regions of overlap with K79+ uHF cells.
(E) Top images, overhead views of skin following incubation with X-gal in cloning cylinders (left) or with cylinders removed (right). Bottom images, whole mounts showing LacZ staining of untreated 8-week-old skin (left), acetone-treated 8-week-old skin (middle), and acetone-treated 20-week-old skin (right). Asterisk, occasional LacZ+ cells in the IFE.
(F) TEM of IFE. Right image is a magnified view showing LGs (arrows).
(G) TEM of uHF. Right image is a magnified view showing LGs (arrows).
Scale bars for (C), (F), and (G), 1 μm; all others, 50 μm.
See also Figure S1.
