Table 2. Information on Loci Used in the Study.
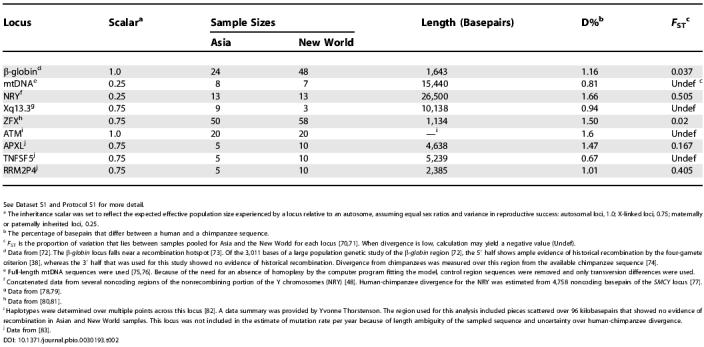
See Dataset S1 and Protocol S1 for more detail.
a The inheritance scalar was set to reflect the expected effective population size experienced by a locus relative to an autosome, assuming equal sex ratios and variance in reproductive success: autosomal loci, 1.0; X-linked loci, 0.75; maternally or paternally inherited loci, 0.25.
b The percentage of basepairs that differ between a human and a chimpanzee sequence.
c F ST is the proportion of variation that lies between samples pooled for Asia and the New World for each locus [70,71]. When divergence is low, calculation may yield a negative value (Undef).
d Data from [72]. The β-globin locus falls near a recombination hotspot [73]. Of the 3,011 bases of a large population genetic study of the β-globin region [72], the 5′ half shows ample evidence of historical recombination by the four-gamete criterion [38], whereas the 3′ half that was used for this study showed no evidence of historical recombination. Divergence from chimpanzees was measured over this region from the available chimpanzee sequence [74].
e Full-length mtDNA sequences were used [75,76]. Because of the need for an absence of homoplasy by the computer program fitting the model, control region sequences were removed and only transversion differences were used.
f Concatenated data from several noncoding regions of the nonrecombining portion of the Y chromosomes (NRY) [48]. Human-chimpanzee divergence for the NRY was estimated from 4,758 noncoding basepairs of the SMCY locus [77].
i Haplotypes were determined over multiple points across this locus [82]. A data summary was provided by Yvonne Thorstenson. The region used for this analysis included pieces scattered over 96 kilobasepairs that showed no evidence of recombination in Asian and New World samples. This locus was not included in the estimate of mutation rate per year because of length ambiguity of the sampled sequence and uncertainty over human-chimpanzee divergence.
j Data from [83].
