Figure 3. Hypothetic mechanism of cycles of binge drinking intoxication increasing pro-inflammatory gene transcription to increasingly compromise neuronal networks that drive the progression to alcohol use disorder (AUD).
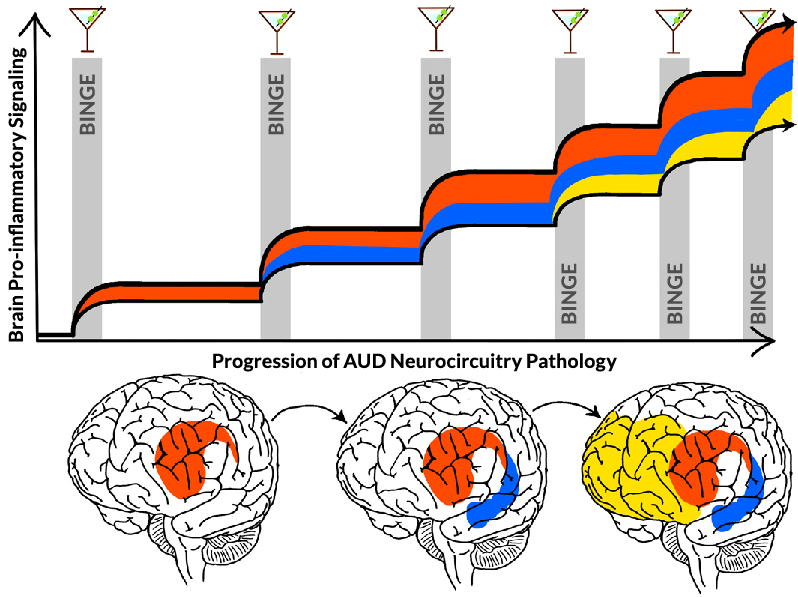
With each binge drinking event (gray bars), pro-inflammatory gene induction and transcription changes increase (adapted from Koob and Volkow1). Initial stages of binge drinking increase HMGB1 release and other signals that sensitize microglia and activate reward and emotional salience networks (red). This activation spreads with further cycles, progressively increasing involvement of emotional-salience networks (blue) as binge drinking increases in frequency. Further cycles may increase pro-inflammatory signaling that compromises cortical executive function networks (yellow). Together, these networks affect domains associated with reward seeking, impulse inhibition, perseveration, and compulsion to drink that occur with AUD. It is unknown, however, whether networks become progressively involved with binge-drinking cycles as depicted here or if each network shows accumulation of pro-inflammatory and network dysfunction with cycles. Note: HMGB1, high mobility group box protein 1.
