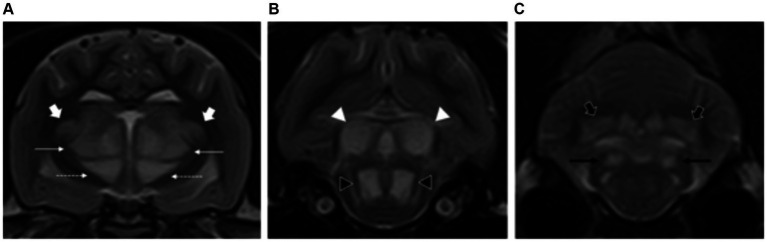
Figure 5.
Transverse plane T2-weighted images of a cat with thiamine deficiency at the level of the thalamus (A), midbrain (B), and cerebellum (C). There are bilateral and symmetric hyperintensities affecting multiple deep grey matter nuclei: lateral geniculate (short white arrows), thalamus (long white arrows), and subthalamus (dashed long white arrow) (A); caudal colliculi (white arrowhead) and oculomotor nuclei (black arrowhead) (B); and cerebellar (short black arrows) and vestibular nuclei (long black arrows) (C).