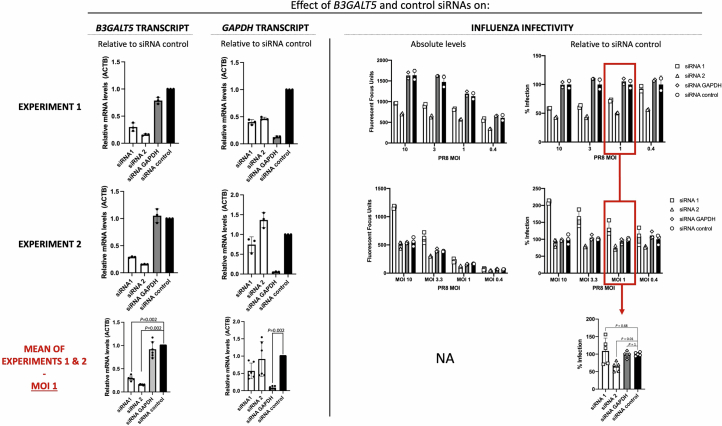
Extended Data Fig. 9. Impact of B3GALT5 siRNA knockdown on influenza infectivity in Calu-3 cells.
In each plot, bars represent the averages across replicates from each experiment (n = 2), points represent the values from the individual replicates (n = 3), and lines show the width of the distribution of the data points. The first column shows mRNA levels of B3GALT5 relative to ACTB transcript in cells treated with four different siRNAs: two targeting B3GALT5 (siRNA1 and siRNA2) and two negative controls (one targeting GAPDH and a scrambled siRNA). The second and third columns show results from infection assay with PR8-GFP (H1N1, multiplicity of infection [MOI] of 0.4 to 10), with the latter column showing infectivity relative to the scrambled siRNA control. The GAPDH siRNA (but not the two siRNAs against B3GALT5) significantly reduced GAPDH expression relative to the scrambled siRNA (~90% reduction). P-values derived from a two-sided Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test and asterisks (*) mark those experiments with P < 0.05.