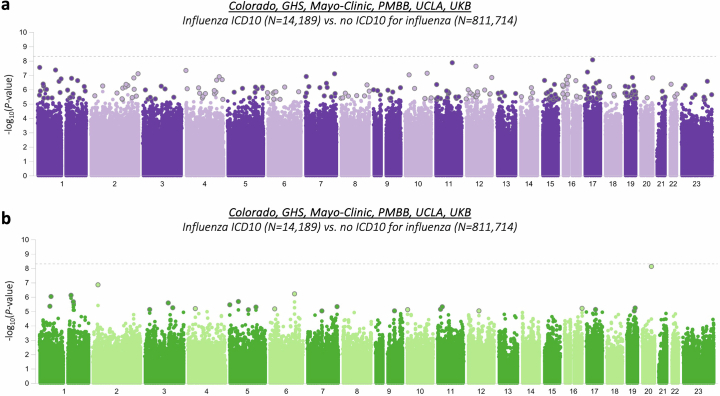
Extended Data Fig. 5. Summary of association results between lifetime medical record-based influenza and rare coding variants from exome sequencing in six biobanks (Colorado, DiscovEHR, Mayo-Clinic, UCLA, UKB, UPENN-PMBB).
We tested 23 million rare (AAF < 1%) variants derived from exome sequencing, comparing 14,189 individuals with (cases) against 811,714 individuals without (controls) an ICD10 code for influenza. a,b, Manhattan plots of (a) individual coding variants (each point represents a single variant) and (b) coding variants tested on aggregate through gene burden tests (each point represents a burden test for a gene, with up to 40 different burden tests performed per gene; Methods). The dotted grey line demarcates P = 2.1 × 10−9 (corresponding to a Bonferroni correction for the number of individual variant and gene-based burden tests performed). Unadjusted P-values derived from Firth-regression (two-sided test) implemented in REGENIE9.