Abstract
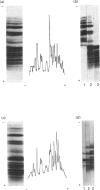
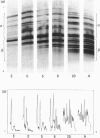
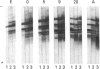
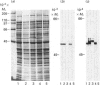
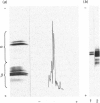
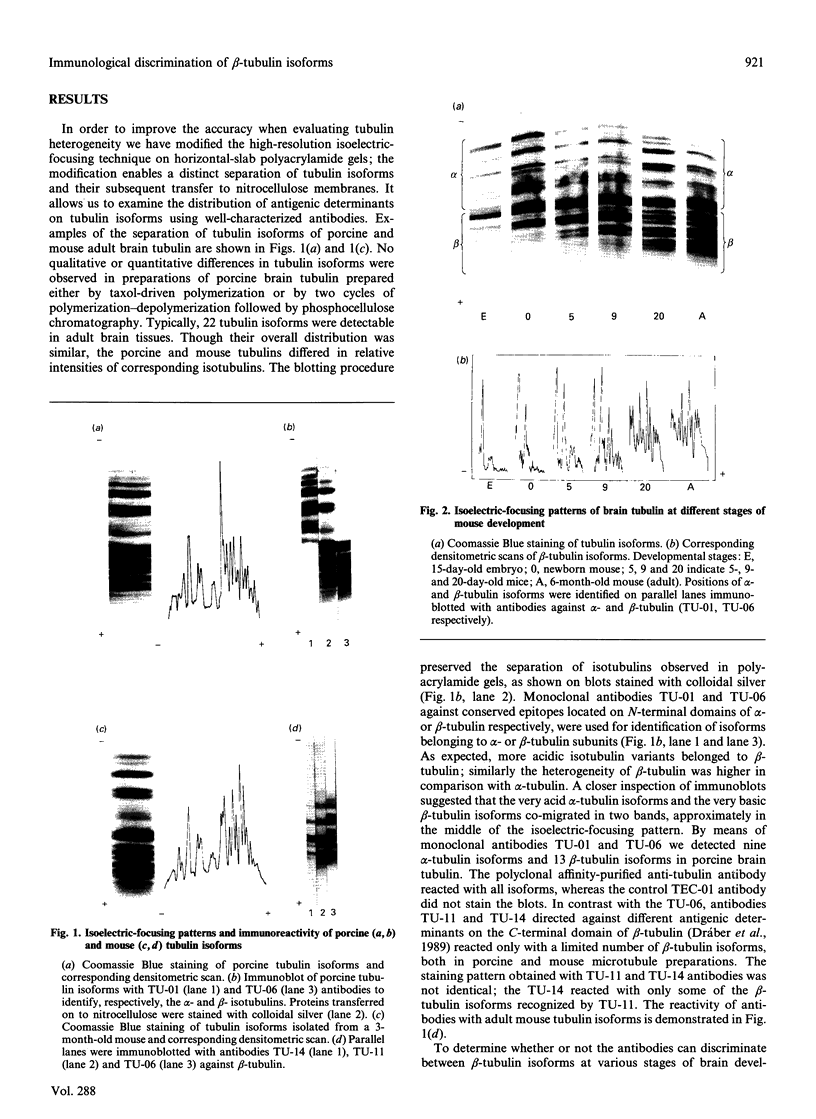
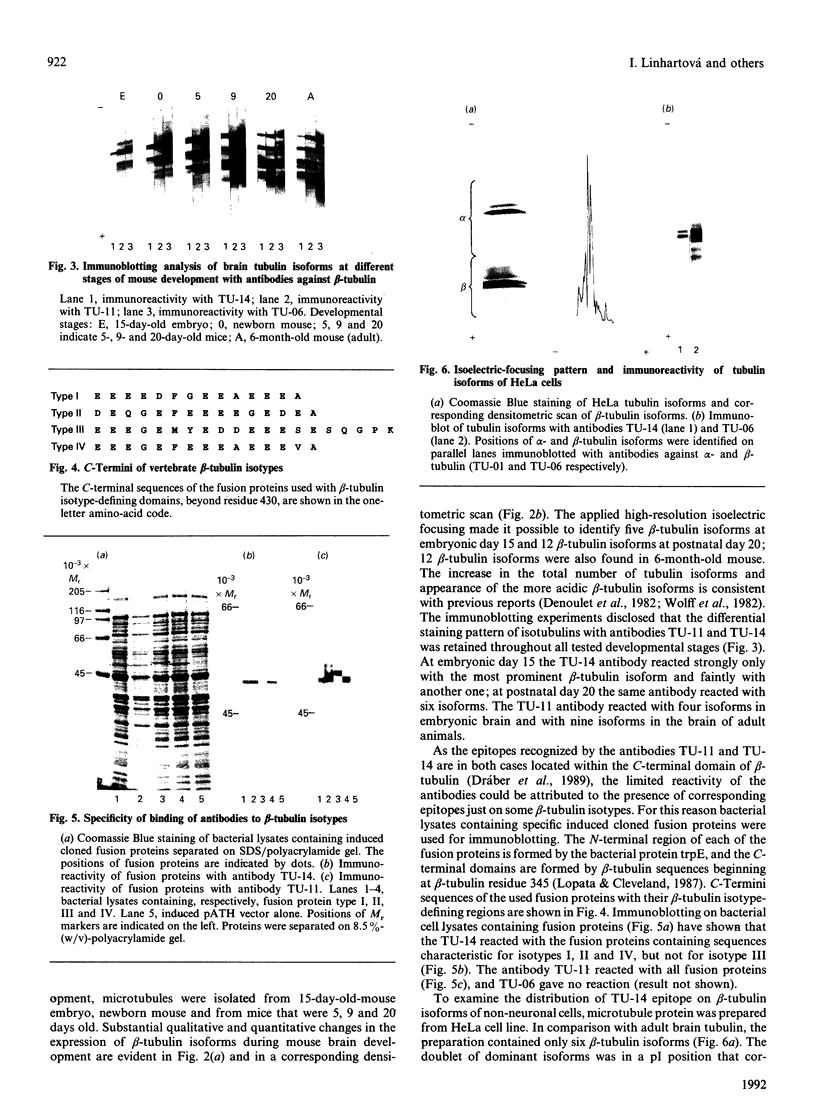
Individual beta-tubulin isoforms in developing mouse brain were characterized using immunoblotting, after preceding high-resolution isoelectric focusing, with monoclonal antibodies against different structural regions of beta-tubulin. Some of the antibodies reacted with a limited number of tubulin isoforms in all stages of brain development and in HeLa cells. The epitope for the TU-14 antibody was located in the isotype-defining domain and was present on the beta-tubulin isotypes of classes I, II and IV, but absent on the neuron-specific class-III isotype. The data suggest that non-class-III beta-tubulins in mouse brain are substrates for developmentally regulated post-translational modifications and that beta-tubulins of non-neuronal cells are also post-translationally modified.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. E., Hunt D. F., Lee M. K., Shabanowitz J., Michel H., Berlin S. C., MacDonald T. L., Sundberg R. J., Rebhun L. I., Frankfurter A. Characterization of posttranslational modifications in neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin by mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4685–4689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asai D. J., Remolona N. M. Tubulin isotype usage in vivo: a unique spatial distribution of the minor neuronal-specific beta-tubulin isotype in pheochromocytoma cells. Dev Biol. 1989 Apr;132(2):398–409. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Roach M. C., Trcka P., Ludueña R. F. Increased microtubule assembly in bovine brain tubulin lacking the type III isotype of beta-tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1794–1799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Roach M. C., Wall K. A., Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Ludueña R. F. A monoclonal antibody against the type II isotype of beta-tubulin. Preparation of isotypically altered tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3029–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barra H. S., Arce C. A., Rodríguez J. A., Caputto R. Some common properties of the protein that incorporates tyrosine as a single unit and the microtubule proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1384–1390. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoulet P., Edde B., Jeantet C., Gros F. Evolution of tubulin heterogeneity during mouse brain development. Biochimie. 1982 Mar;64(3):165–172. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dráber P., Dráberová E., Linhartová I., Viklický V. Differences in the exposure of C- and N-terminal tubulin domains in cytoplasmic microtubules detected with domain-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1989 Mar;92(Pt 3):519–528. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.3.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dráber P., Dráberová E., Viklický V. Immunostaining of human spermatozoa with tubulin domain-specific monoclonal antibodies. Recognition of a unique beta-tubulin epitope in the sperm head. Histochemistry. 1991;95(5):519–524. doi: 10.1007/BF00315749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dráber P., Lagunowich L. A., Dráberová E., Viklický V., Damjanov I. Heterogeneity of tubulin epitopes in mouse fetal tissues. Histochemistry. 1988;89(5):485–492. doi: 10.1007/BF00492606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dráber P., Pokorná Z. Differentiation antigens of mouse teratocarcinoma stem cells defined by monoclonal antibodies. Cell Differ. 1984 Dec;15(2-4):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(84)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Nido J., Serrano L., López-Otín C., Vandekerckhove J., Avila J. Phosphorylation of a neuronal-specific beta-tubulin isotype. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13949–13954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddé B., Rossier J., Le Caer J. P., Desbruyères E., Gros F., Denoulet P. Posttranslational glutamylation of alpha-tubulin. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.1967194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field D. J., Collins R. A., Lee J. C. Heterogeneity of vertebrate brain tubulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4041–4045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field D. J., Lee J. C. Analysis of tubulin proteins and peptides in neuronal and non-neuronal tissues using immobilized pH gradients. Electrophoresis. 1988 Sep;9(9):555–562. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George H. J., Misra L., Field D. J., Lee J. C. Polymorphism of brain tubulin. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2402–2409. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi H. C., Cleveland D. W. Differential utilization of beta-tubulin isotypes in differentiating neurites. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):663–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi H. C., Cleveland D. W. Diversity among tubulin subunits: toward what functional end? Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;16(3):159–163. doi: 10.1002/cm.970160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Hernault S. W., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas alpha-tubulin is posttranslationally modified by acetylation on the epsilon-amino group of a lysine. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):473–478. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. K., Rebhun L. I., Frankfurter A. Posttranslational modification of class III beta-tubulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7195–7199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. K., Tuttle J. B., Rebhun L. I., Cleveland D. W., Frankfurter A. The expression and posttranslational modification of a neuron-specific beta-tubulin isotype during chick embryogenesis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;17(2):118–132. doi: 10.1002/cm.970170207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Gu W., Cowan N. J. Free intermingling of mammalian beta-tubulin isotypes among functionally distinct microtubules. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W. In vivo microtubules are copolymers of available beta-tubulin isotypes: localization of each of six vertebrate beta-tubulin isotypes using polyclonal antibodies elicited by synthetic peptide antigens. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1707–1720. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueña R. F., Zimmermann H. P., Little M. Identification of the phosphorylated beta-tubulin isotype in differentiated neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeremans M., Daneels G., De Mey J. Sensitive colloidal metal (gold or silver) staining of protein blots on nitrocellulose membranes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Mar;145(2):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Obar R. A., Vallee R. B. Interaction of brain cytoplasmic dynein and MAP2 with a common sequence at the C terminus of tubulin. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):569–572. doi: 10.1038/342569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Fuller M. T. Monoclonal antibodies specific for an acetylated form of alpha-tubulin recognize the antigen in cilia and flagella from a variety of organisms. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2085–2094. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raybin D., Flavin M. An enzyme tyrosylating alpha-tubulin and its role in microtubule assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):1088–1095. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L., Bhattacharyya B., Wolff J. Tubulin subunit carboxyl termini determine polymerization efficiency. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):43–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanker L. H., Vanderlaan M., Juarez-Salinas H. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascites fluid by hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jan 21;76(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. F. Structure and utilization of tubulin isotypes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:687–716. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.003351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B. A taxol-dependent procedure for the isolation of microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):435–442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff A., Denoulet P., Jeantet C. High level of tubulin microheterogeneity in the mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Aug 31;31(3):323–328. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Viña S., Andreu D., Medrano F. J., Nieto J. M., Andreu J. M. Tubulin structure probed with antibodies to synthetic peptides. Mapping of three major types of limited proteolysis fragments. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5352–5365. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]