Figure 1.
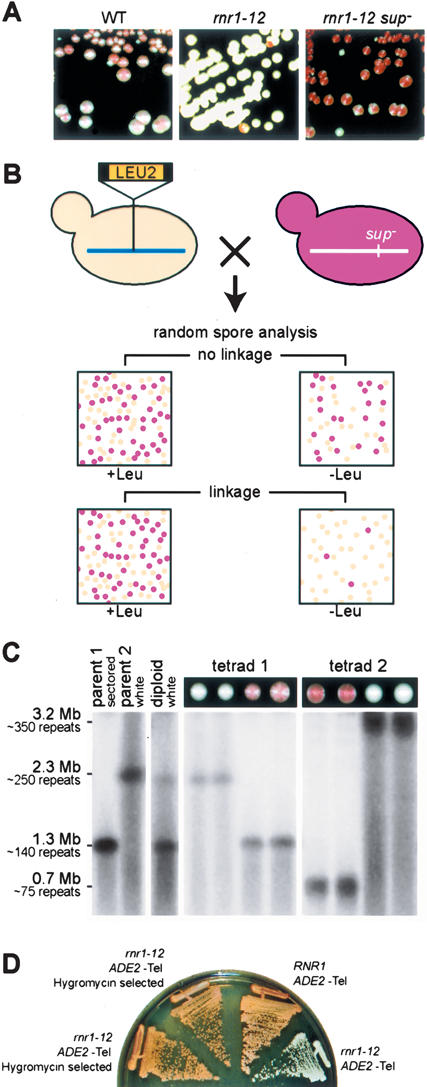
Spontaneous suppressors of telomeric position effect (TPE) loss in rnr1-12 mutants are due to large rDNA repeat deletions. (A) Wild-type (WT) cells with ADE2-Tel (left panel), rnr1-12 ADE2-Tel cells (middle panel), and TPE suppressors (rnr1-12 ADE2-Tel sup–), which are stable upon restreaking (right panel). (B) Strategy for genetic mapping of TPE suppressor mutations. The linkage between the LEU2 marker and the SUP gene is assessed by random spore analysis. Fifty percent of the Leu+ spores are sectored in the absence of linkage. This ratio decreases in the event of linkage. (C) The TPE suppressor phenotype segregates 2:2 in backcrosses to a parental strain and is associated with a short rDNA cluster. Analysis of two complete tetrads from a cross between YAM70 (parent 1, rnr1-12 sup– ADE2-Tel) and YAM97 (parent 2, rnr1-12 ADE2-Tel). DNA from the indicated strains was analyzed by PFGE of BamHI-digested plugs. The rDNA cluster was detected by Southern blotting using a radiolabeled rDNA probe. (D) rnr1-12 ADE2-Tel cells (YAM97) were subjected to Hygromycin-resistance selection for short rDNA. The TPE phenotypes of two such HygR clones (left) were then compared with otherwise isogenic RNR1 and rnr1-12 strains (right).
