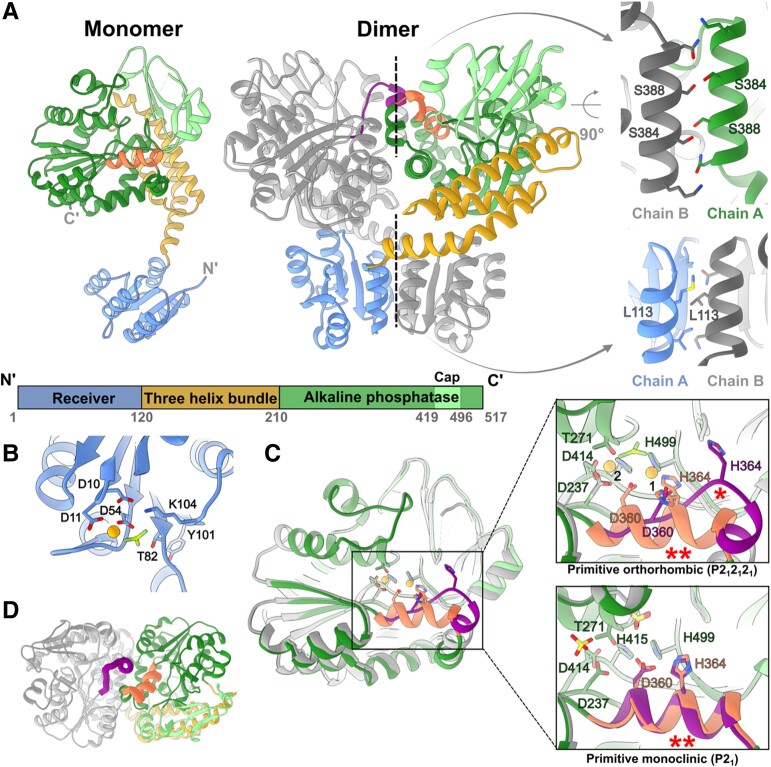
Fig. 1.
Crystal structures of PorXFJ. A) Monomeric and dimeric assembly of PorXFJ. One monomer is colored according to the different domains, while the other monomer is in gray. The two dimeric interfaces are labeled by dashed lines, and their zoom-in views highlight crucial residues at these dimerization interfaces. B) Phosphorylation site at the REC domain. The conserved Asp54 coordinates both the phosphomimetic BeF3 molecule and a divalent cation presented as an orange sphere. Additional residues involved in coordination and stabilization of the phosphorylation site are presented. C) Structural variation of the APS domain in the different monomers. Overlay of different APS domain conformers demonstrate the observed conformational change in residues 358–369. In the zoom-in views of the catalytic site, key residues associated with the coordination of two divalent cations (binding sites labeled as 1 and 2) and substrate binding/catalysis are presented. The substrate-mimicking BeF3 ion (shades of green) or sulfate ion (yellow), specifically identified in different PorXFJ crystals, is presented separately. The alternative conformation of residues 358–369, labeled by (*), disrupts the optimal positioning of the conserved divalent cation coordinating residues, Asp360 and His364. The helical conformation of residues 358–369, which maintains the ideal position of Asp360 and His364, is labeled by (**). D) A top view of the APS domains in the PorXFJ dimer demonstrates a conformational change in residues 358–369 (colored in purple and orange in each monomer), located in close proximity to the APS domain dimerization interface.