FIGURE 1.
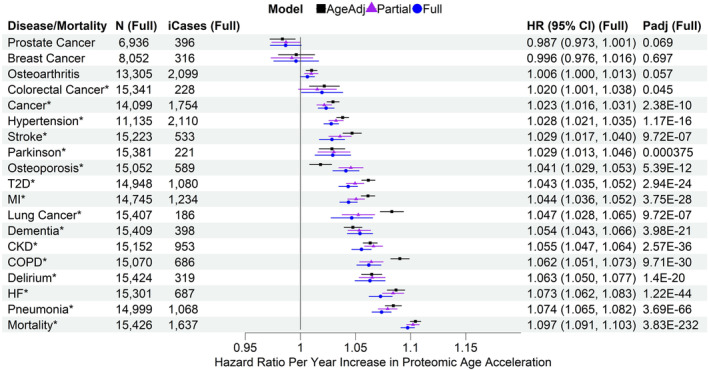
Associations of PAC proteomic age acceleration with all‐cause mortality and incident diseases in the test set sample. CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; HF, heart failure; MI, myocardial infarction; T2D, type 2 diabetes. N (Full): sample size with complete data for the fully adjusted model, after excluding participants diagnosed with the disease at or prior to baseline. iCases (Full): number of incident cases of N samples. Cox regression model for all‐cause mortality and Fine‐Gray subdistribution hazard models to account for the effect of death on the risk for incident diseases, adjusting for different sets of covariates at baseline (age‐adjusted, partially adjusted, and fully adjusted models). AgeAdj: chronological age; Partial: chronological age, sex, ethnicity, education, Townsend deprivation index, smoking status, and body mass index; Full: covariates in the partially adjusted model, and pre‐existing diseases (hypertension, myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke, type 2 diabetes, COPD, pneumonia, chronic kidney disease, any cancer excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer, dementia, and Parkinson's disease, without delirium as there were only two samples with a history of delirium at baseline in the test set sample). Padj (Full): p‐values adjusted for multiple testing (tests based on age‐adjusted, partially adjusted, and fully adjusted models for all‐cause mortality and incident diseases). Disease/all‐cause mortality highlighted with asterisk (*) if p adj <0.05.
