Figure 3.
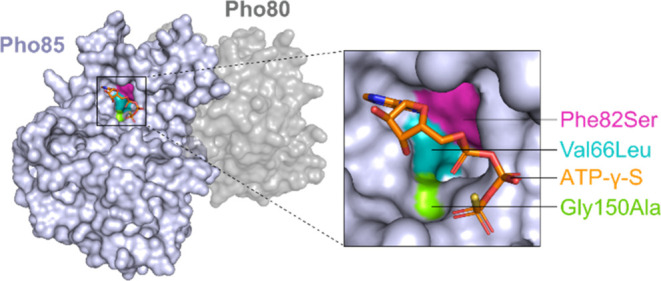
Residue conservation analysis identified three putative resistance mutations in the active site of the CDK ETaG (Table 1), suggesting that the product of the ros BGC is an active site, ATP-competitive inhibitor of CDKs. Mutations are mapped onto the structure of the yeast Pho85-Pho80 CDK-Cyclin complex (PDB ID 2PMI).25
