Fig. 3 |. Application of MAJESTIC for delivery of different therapeutic transgenes into T human cells.
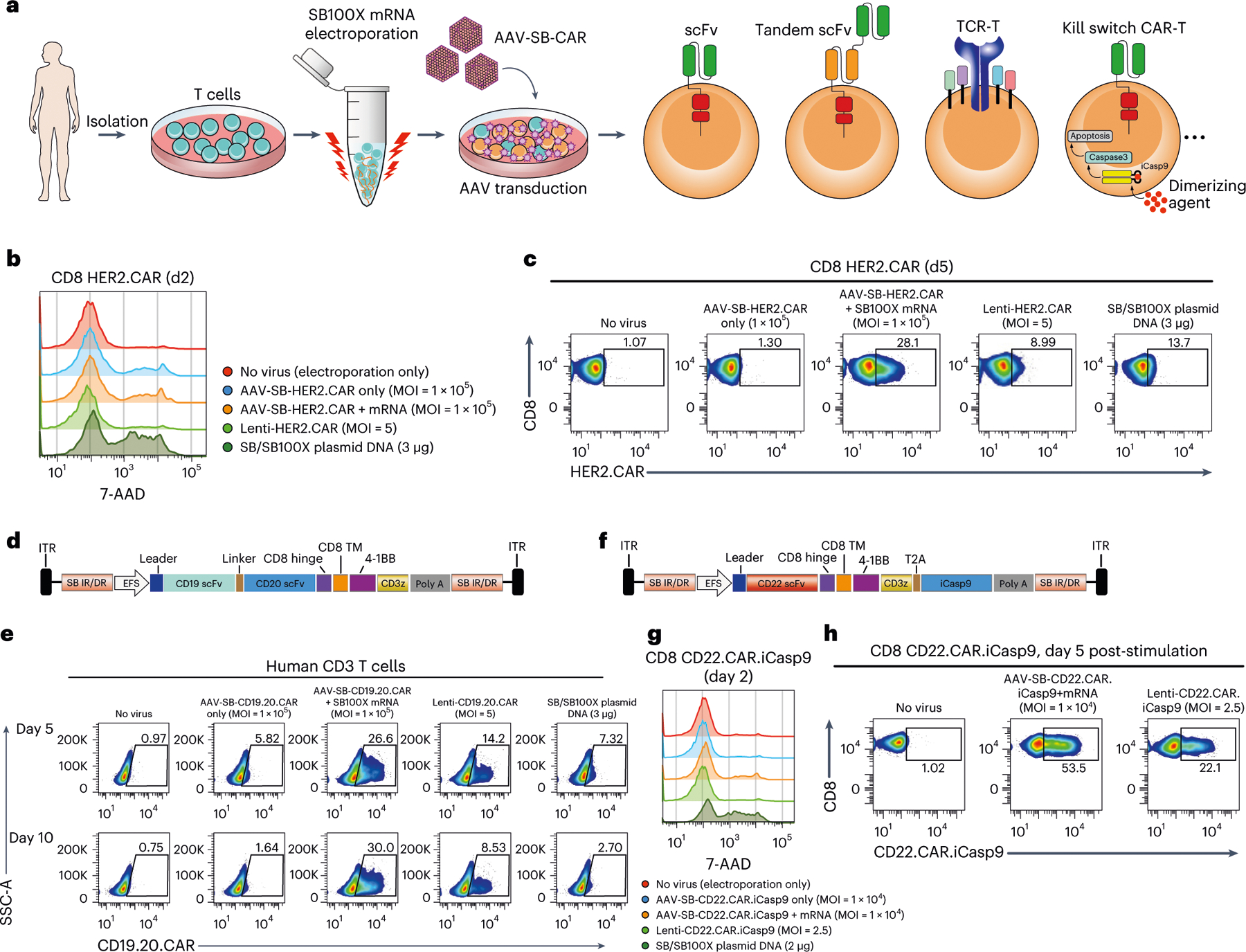
a, Schematic of various therapeutic cells (that is, single scFv CAR, tandem scFv CAR, TCR-T and kill-switch CAR) that can be generated via the AAV-SB system. b, Flow cytometry and histogram overlays of cell viability post-electroporation as measured with 7-AAD staining. c, Representative flow cytometry plots of HER2.CAR T cells. d, Schematic representation of the AAV-SB-CD19.20.CAR construct. CD19 scFv and CD20 scFv CAR sequences are joined by a linker and are expressed together as a tandem scFv CAR. e, Representative flow cytometry plots to evaluate CAR expression of CD19.20.CAR T cells. f, Schematic representation of the AAV-SB-HER2.CAR. iCasp9 construct. g, Flow cytometry and histogram overlays of cell viability post-electroporation as measured with 7-AAD staining. h, Representative flow cytometry plots of CD22.CAR.iCasp9 T cells post antigen-specific cancer cells stimulation. In this figure, each assay was done with one donor with three to five technical replicates; donor 2 T cells were used for b and c; donor VP2 T cells were used for d and e; donor 2 T cells were used for g and h.
