Abstract
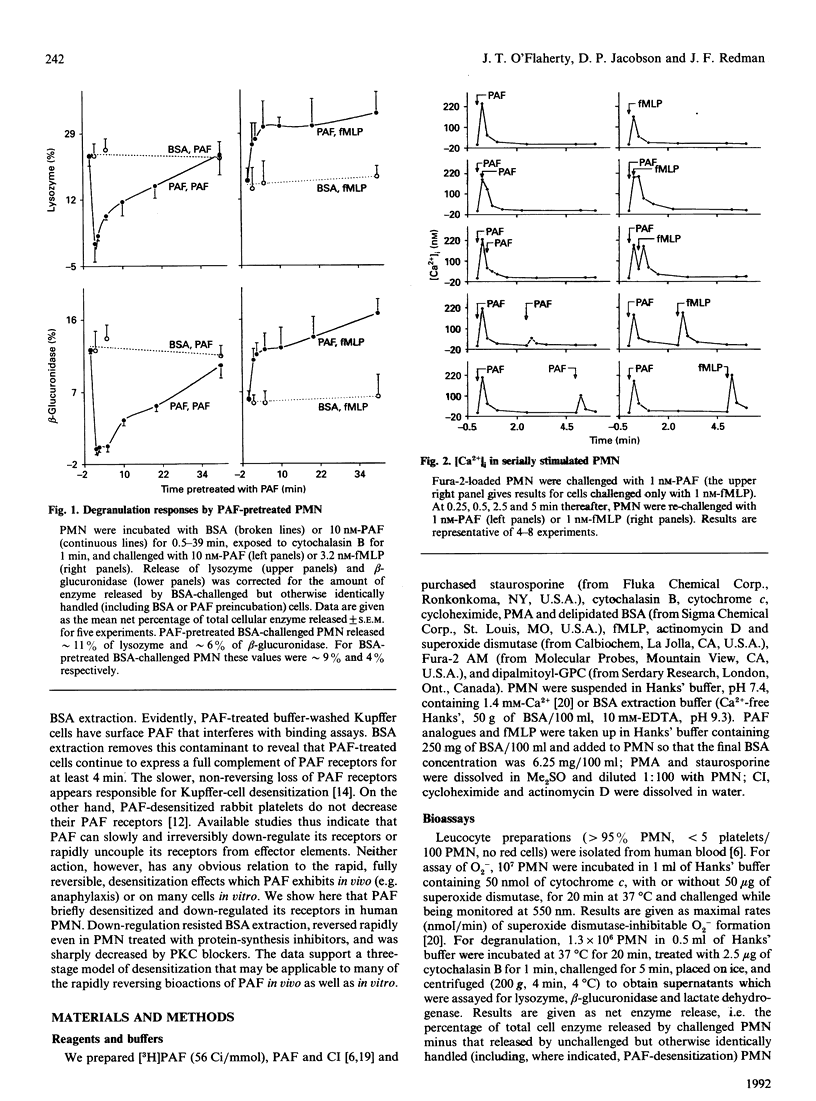
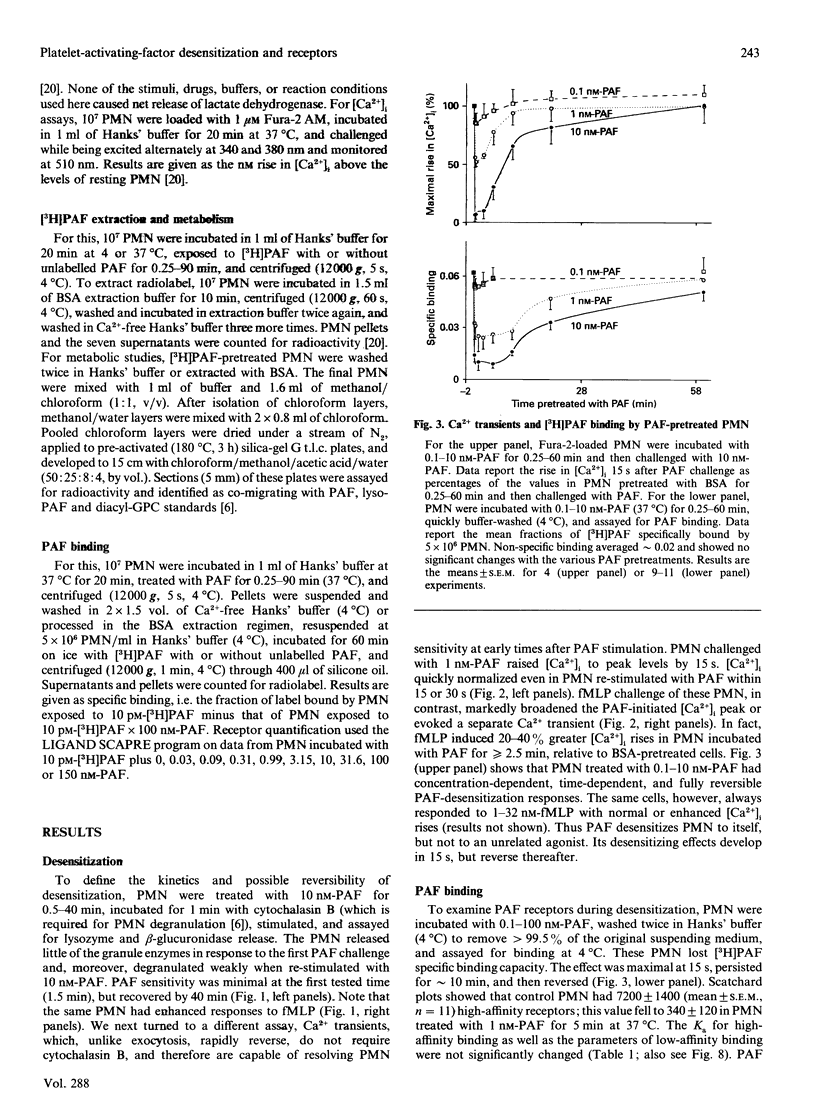
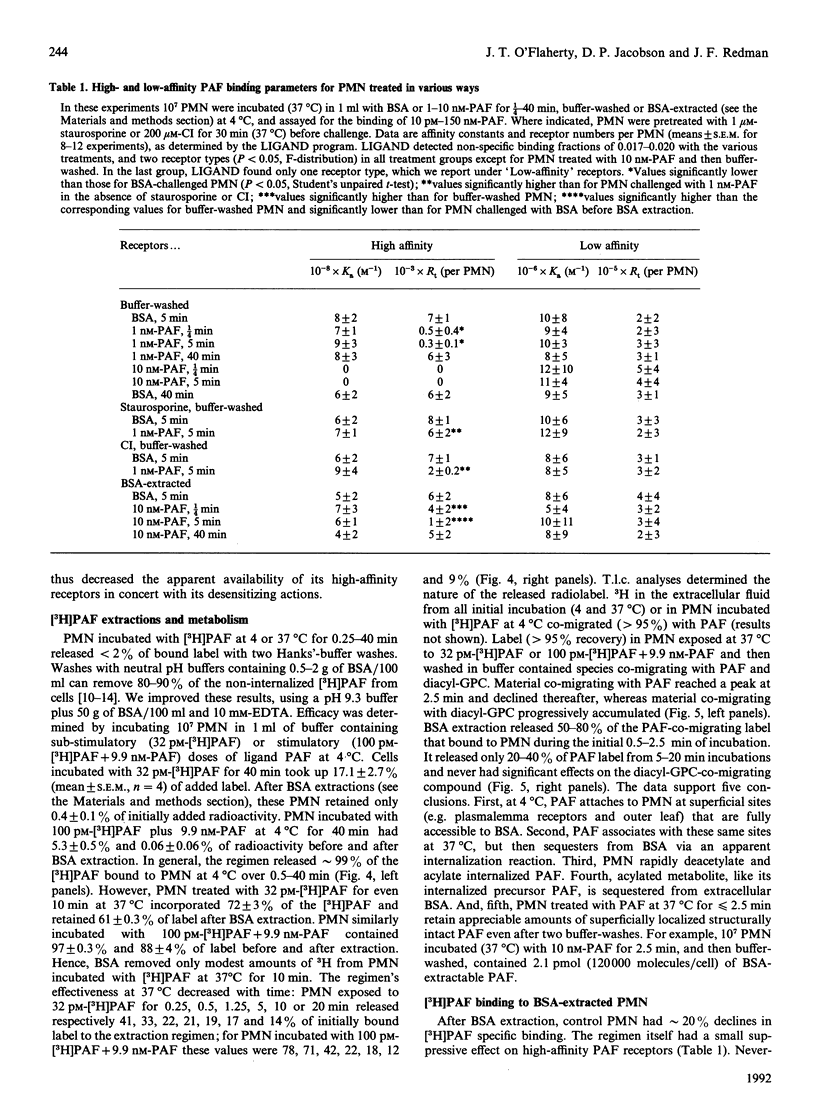
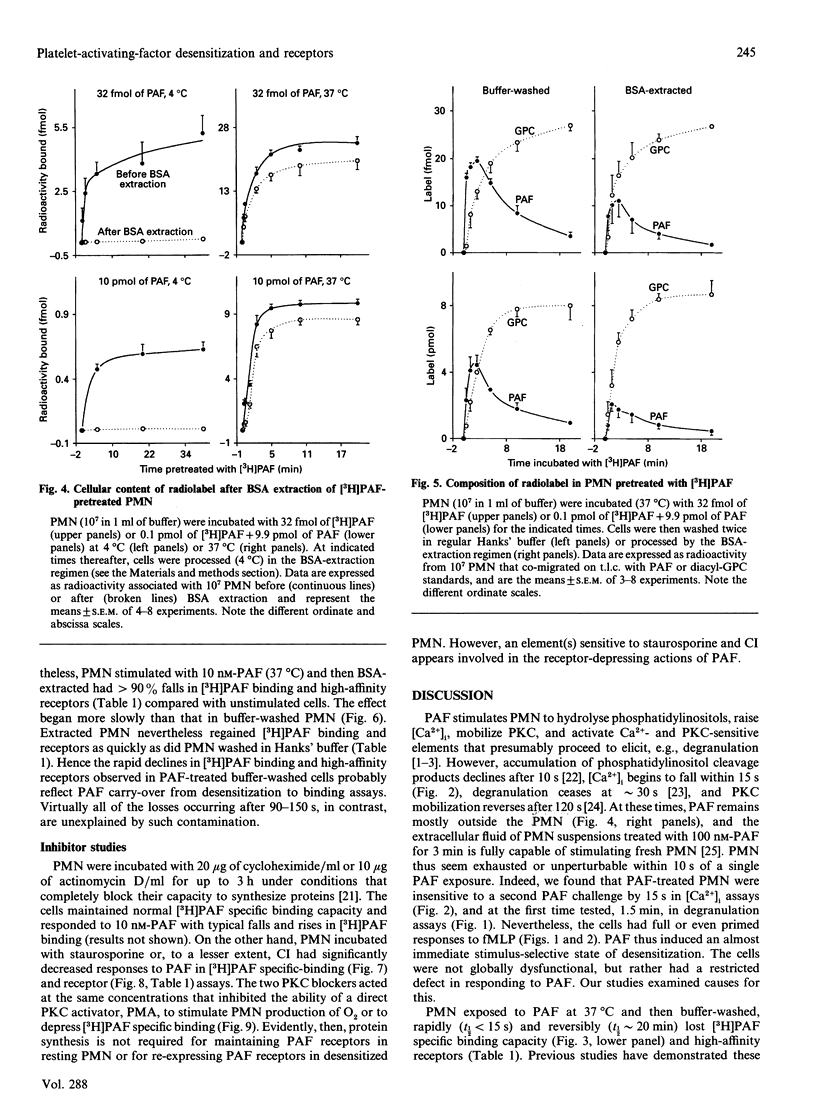
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) desensitizes as well as stimulates its various target cells, We find that human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) exposed to PAF became maximally unresponsive to a second PAF challenge within 15-90 s in assays of Ca2+ mobilization and degranulation. The cells regained full PAF-sensitivity over the ensuing 20-40 min. These effects correlated with changes in PAF receptor availability. PMN treated with PAF, washed in regular buffer and assayed for PAF binding exhibited falls (maximal in 15 s), followed by rises (reaching control levels by 60 min), in the number of high-affinity PAF receptors. However, tracking studies showed that [3H]PAF accumulated on the cell surface for approximately 2 min before being internalized. Regular-buffer washes did not remove this superficial PAF, whereas a washing regimen using excess albumin to adsorb PAF removed 99% of the surface compound. PMN washed by the latter regimen after PAF exposure lost PAF receptors relatively slowly (maximal at approximately 5 min), but the ultimate extent of this loss and the rate at which receptor expression normalized were similar to those of cells washed in regular buffer. Neither cycloheximide nor actinomycin D influenced the course of the receptor changes, but two protein kinase C (PKC) blockers, staurosporine and 1-(5-isoquinolinesulphonyl)piperazine, inhibited the receptor-receptor-depleting actions of PAF. Indeed, a phorbol diester activator of PKC also caused PMN to decrease high-affinity PAF receptor numbers, and the two PKC blockers antagonized this action at concentrations that inhibited PAF-induced PAF receptor losses. We conclude that: (a) PAF induces PMN to down-regulate and then to re-express PAF receptors independently of protein synthesis; (b) these changes are likely to underlie the later stages and reversal of desensitization; (c) the onset (t < or = 2 min) of desensitization, however, precedes receptor down-regulation and must be due to receptor uncoupling from transductional elements; and (d) down-regulation of receptors for PAF appears to be mediated by PKC and/or elements inhibited by PKC blockers.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratton D. L., Kailey J. M., Clay K. L., Henson P. M. A model for the extracellular release of PAF: the influence of plasma membrane phospholipid asymmetry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 11;1062(1):24–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90330-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Harwood J. P., Aguilera G., Dufau M. L. Hormonal regulation of peptide receptors and target cell responses. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):109–116. doi: 10.1038/280109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W., Liu H., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Regulation of platelet-activating factor receptor and PAF receptor-mediated arachidonic acid release by protein kinase C activation in rat Kupffer cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Oct;282(1):188–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W., Liu H., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Regulation of platelet-activating factor receptors in rat Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20448–20457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay K. L., Johnson C., Henson P. Binding of platelet activating factor to albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 1;1046(3):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90246-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi C. R., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Two distinct pathways of platelet-activating factor-induced hydrolysis of phosphoinositides in primary cultures of rat Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18234–18241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. C., Beckman J. K., Zaboy K. A., Lukens J. N. Modulation of neutrophil oxidative responses to soluble stimuli by platelet-activating factor. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):931–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. C., Stitt E. S. Enhancement of phorbol ester-induced protein kinase activity in human neutrophils by platelet-activating factor. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Dec;137(3):439–447. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. C., Stitt E. S. Platelet-activating factor induces protein kinase activity in the particulate fraction of human neutrophils. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., McPhail L. C., Marfat A., Stimler-Gerard N. P., Bass D. A., McCall C. E. Role of protein kinases in stimulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte oxidative metabolism by various agonists. Differential effects of a novel protein kinase inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):61–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI112302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma H., Hanahan D. J. Attenuation of platelet activating factor (PAF)-induced stimulation of rabbit platelet GTPase by phorbol ester, dibutyryl cAMP, and desensitization: concomitant effects on PAF receptor binding characteristics. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Apr;262(1):32–39. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma H., Tokumura A., Hanahan D. J. Binding and internalization of platelet-activating factor 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine in washed rabbit platelets. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10582–10587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B. Specific receptors of platelet-activating factor, receptor heterogeneity, and signal transduction mechanisms. J Lipid Mediat. 1990 May-Jul;2(3-4):123–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramp W., Pieroni G., Pinckard R. N., Hanahan D. J. Observations on the critical micellar concentration of 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine and a series of its homologs and analogs. Chem Phys Lipids. 1984 May;35(1):49–62. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(84)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachachi H., Plantavid M., Simon M. F., Chap H., Braquet P., Douste-Blazy L. Inhibition of transmembrane movement and metabolism of platelet activating factor (PAF-acether) by a specific antagonist, BN 52021. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 30;132(2):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Carpenter C. D., Gill G. N., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Protein kinase C phosphorylation at Thr 654 of the unoccupied EGF receptor and EGF binding regulate functional receptor loss by independent mechanisms. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):839–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord P. C., Wilmoth L. M., Mizel S. B., McCall C. E. Expression of interleukin-1 alpha and beta genes by human blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1312–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI115134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love J. T., Jr, Padula S. J., Lingenheld E. G., Amin J. K., Sgroi D. C., Wong R. L., Sha'fi R. I., Clark R. B. Effects of H-7 are not exclusively mediated through protein kinase C or the cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91973-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Wyatt J., Mel S. F., Rossi M. E., Shohet S. B. Lipid translocation across the human erythrocyte membrane. Regulatory factors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6537–6543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Chabot M. C., Redman J., Jr, Jacobson D., Wykle R. L. Receptor-independent metabolism of platelet-activating factor by myelogenous cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Jacobson D. P., Redman J. F. Bidirectional effects of protein kinase C activators. Studies with human neutrophils and platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6836–6843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Lees C. J., Miller C. H., McCall C. E., Lewis J. C., Love S. H., Wykle R. L. Selective desensitization of neutrophils: further studies with 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine analogues. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):731–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Nishihira J. Arachidonate metabolites, platelet-activating factor, and the mobilization of protein kinase C in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1889–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Redman J. F., Jacobson D. P., Rossi A. G. Stimulation and priming of protein kinase C translocation by a Ca2+ transient-independent mechanism. Studies in human neutrophils challenged with platelet-activating factor and other receptor agonists. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21619–21623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Rossi A. G., Jacobson D. P., Redman J. F. Roles of Ca2+ in human neutrophil responses to receptor agonists. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):705–711. doi: 10.1042/bj2770705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Rossi A. G., Redman J. F., Jacobson D. P. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha regulates expression of receptors for formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, leukotriene B4, and platelet-activating factor. Dissociation from priming in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3842–3847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Surles J. R., Redman J., Jacobson D., Piantadosi C., Wykle R. L. Binding and metabolism of platelet-activating factor by human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):381–388. doi: 10.1172/JCI112588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paubert-Braquet M., Koltz P., Guilbaud J., Hosford D., Braquet P. Platelet-activating factor amplifies tumour necrosis factor-induced superoxide generation by human neutrophils. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;264:275–282. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5730-8_45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17381–17384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyne N. J., Murphy G. J., Milligan G., Houslay M. D. Treatment of intact hepatocytes with either the phorbol ester TPA or glucagon elicits the phosphorylation and functional inactivation of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 16;243(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi A. G., Redman J. F., Jacobson D. P., O'Flaherty J. T. Enhancement of human neutrophil responses to platelet activating factor by 5(S)-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoate. J Lipid Mediat. 1991 Sep-Oct;4(2):165–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sako T., Tauber A. I., Jeng A. Y., Yuspa S. H., Blumberg P. M. Contrasting actions of staurosporine, a protein kinase C inhibitor, on human neutrophils and primary mouse epidermal cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4646–4650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E., Haest C. W., Deuticke B. Transbilayer reorientation of platelet-activating factor in the erythrocyte membrane. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwertschlag U. S., Whorton A. R. Platelet-activating factor-induced homologous and heterologous desensitization in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13791–13796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder F. Biochemistry of platelet-activating factor: a unique class of biologically active phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Feb;190(2):125–135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-190-42839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumura A., Tsutsumi T., Yoshida J., Tsukatani H. Translocation of exogenous platelet-activating factor and its lyso-compound through plasma membranes is a rate-limiting step for their metabolic conversions into alkylacylglycerophosphocholines in rabbit platelets and guinea-pig leukocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 1;1044(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90223-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallari D. S., Austinhirst R., Snyder F. Development of specific functionally active receptors for platelet-activating factor in HL-60 cells following granulocytic differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4261–4265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. S., Mandel D. M., Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Evidence for the role of platelet-activating factor in immune complex vasculitis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):669–678. doi: 10.1172/JCI113931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki M., Gomez-Cambronero J., Durstin M., Molski T. F., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate inhibits binding of leukotriene B4 and platelet-activating factor and the responses they induce in neutrophils: site of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5791–5794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


