Abstract
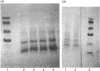
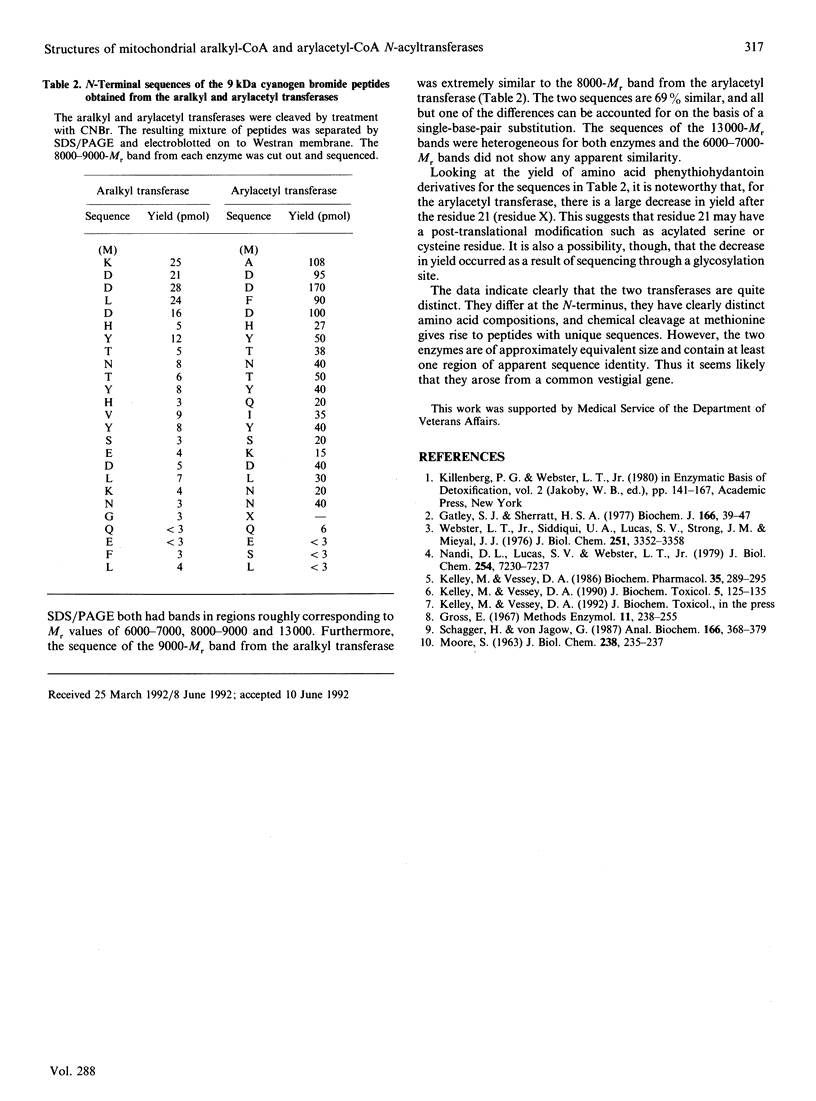
The aralkyl and arylacetyl transferases were purified to homogeneity from bovine kidney by a slight modification of a previous procedure. The M(r) of the arylacetyl transferase was estimated to be 33,500 by SDS/PAGE and that of the aralkyl transferase to be 33,750 by a combination of SDS/PAGE and gel-filtration analysis. N-Terminal-sequence analysis indicated a blocked N-terminus for the arylacetyl transferase and gave the following sequence for the aralkyl transferase: M-F-L-L-Q-G-A-Q-M-L-Q-M-L-E-K. Amino acid analysis revealed differences in composition between the two enzymes. Most notable was the fact that the aralkyl transferase had more methionine and leucine. This difference could be partially accounted for by assuming that the methionine-and-leucine-rich N-terminus was missing from the arylacetyl transferase. Chemical cleavage of the two enzymes at methionine residues using CNBr gave rise to several peptides for each enzyme. N-Terminal-sequence analysis of the 8000-M(r) peptide from the arylacetyl transferase gave a sequence with 69% similarity to the 9000-M(r) peptide from the aralkyl transferase. This was taken to indicate a common origin for the two enzymes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gatley S. J., Sherratt H. S. The synthesis of hippurate from benzoate and glycine by rat liver mitochondria. Submitochondrial localization and kinetics. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 15;166(1):39–47. doi: 10.1042/bj1660039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M., Vessey D. A. Interaction of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate (2,4-D) and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetate (2,4,5-T) with the acyl-CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase enzymes of bovine liver mitochondria. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 15;35(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90528-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M., Vessey D. A. The effects of ions on the conjugation of xenobiotics by the aralkyl-CoA and arylacetyl-CoA N-acyltransferases from bovine liver mitochondria. J Biochem Toxicol. 1990 Summer;5(2):125–135. doi: 10.1002/jbt.2570050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi D. L., Lucas S. V., Webster L. T., Jr Benzoyl-coenzyme A:glycine N-acyltransferase and phenylacetyl-coenzyme A:glycine N-acyltransferase from bovine liver mitochondria. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7230–7237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster L. T., Siddiqui U. A., Lucas S. V., Strong J. M., Mieyal J. J. Identification of separate acyl- CoA:glycine and acyl-CoA:L-glutamine N-acyltransferase activities in mitochondrial fractions from liver of rhesus monkey and man. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 10;251(11):3352–3358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]