Figure 3.
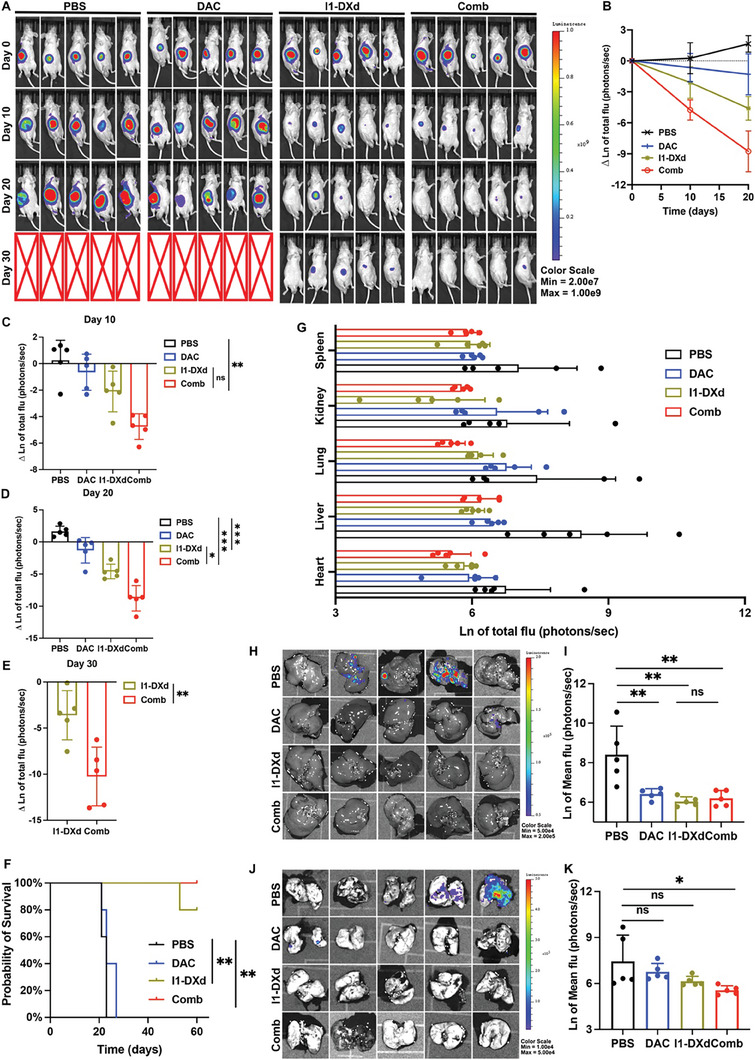
I1‐DXd monotherapy or in combination with DAC inhibits melanoma metastasis and improves survival in mice bearing A375‐luc xenograft tumors. (A) Representative bioluminescent images of mice A375‐luc xenograft tumors in different groups at different time points after injection; (B) Bioluminescence signal intensity at different time points in different groups (n = 5 per group); (C) Quantitative analysis of natural logarithm of tumor bioluminescence signal intensity in different groups at day 10. **p < 0.01; Bonferroni‐adjusted p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (D) Quantitative analysis of natural logarithm of tumor bioluminescence signal intensity in different groups at day 20. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; Bonferroni‐adjusted p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (E) Quantitative analysis of natural logarithm of tumor bioluminescence signal intensity in different groups at day 30. **p < 0.01. (F) Kaplan–Meier survival curve of mice in different groups; (G) Bioluminescence signal intensity of major organs (heart, liver, lung, kidney and spleen) when mice were sacrificed in different groups; (H) Representative bioluminescence images of liver in different groups; (I) Quantitative analysis of liver metastasis burden as depicted from natural logarithm of bioluminescence signal intensity. **p < 0.01; Bonferroni‐adjusted p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (J) Representative bioluminescence images of lung in different groups; (K) Quantitative analysis of lung metastasis burden as depicted from natural logarithm of bioluminescence signal intensity. *p < 0.05; Bonferroni‐adjusted p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
