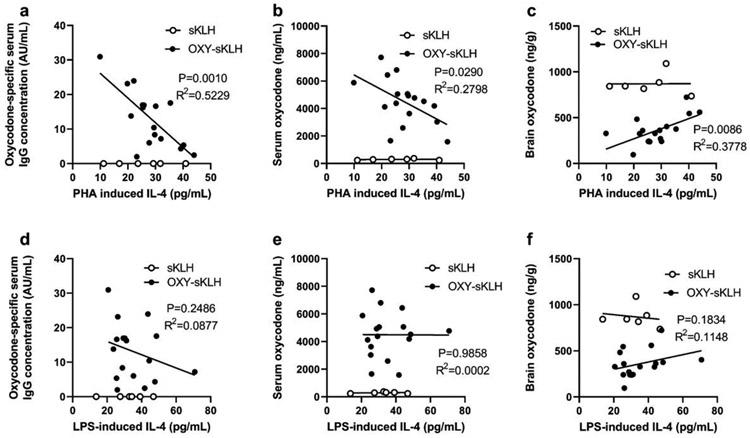
Figure 5. Pre-immunization IL-4 concentration correlates with vaccine efficacy in mice.
Jackson outbred diversity mice (J:DO) mice were bled pre-immunization, and whole blood was plated for in vitro stimulation with either PHA (to stimulate T cells) or LPS (to stimulate innate immune cells). After 24 hours, supernatant was collected, and IL-4 was measured via ELISA. Mice (n=18 active immunization, 6 control immunization) were then immunized 3 times and blood was collected 7 days after the final immunization. Oxycodone-specific IgG concentration was measured by ELISA. Mice were subsequently challenged with oxycodone (2.25 mg/kg, s.c.), and blood and brain were collected 30 minutes post-challenge to measure concentration of oxycodone via LC-MS/MS. Linear correlation between A) oxycodone-specific IgG concentration and PHA-induced IL-4, B) post-challenge serum oxycodone concentration and PHA induced IL-4, and C) post-challenge brain oxycodone concentration and PHA induced IL-4. There was no linear correlation between D) oxycodone-specific IgG concentration and LPS-induced IL-4, E) post-challenge serum oxycodone concentration and LPS-induced IL-4, or F) post-challenge brain oxycodone concentration and LPS-induced IL-4. Linear associations determined via Pearson correlation. Data are from one independent experiment.