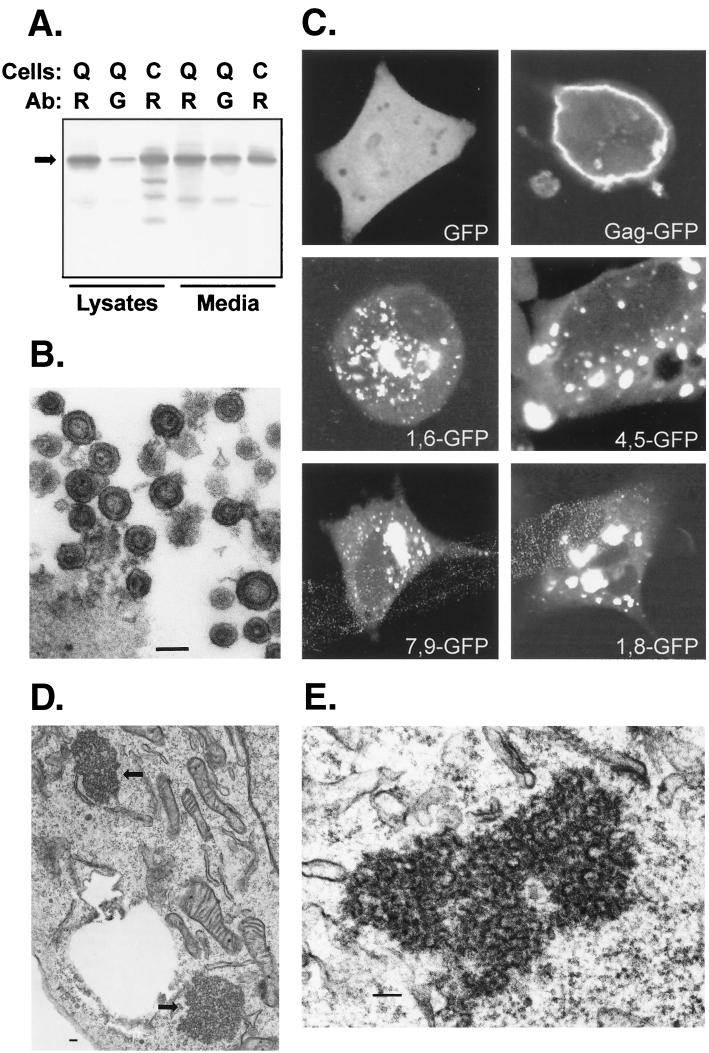
FIG. 4.
Subcellular distribution of M domain mutants. GFP was fused in place of the PR domain of RSV Gag (Fig. 1). (A) Biochemical analysis of Gag-GFP (arrow, 88 kDa) released from QT6 (Q) or COS-1 (C) cells. Immunoprecipitations were performed using polyclonal anti-RSV (R) or polyclonal anti-GFP (G) antibody (Ab) as in Fig. 3. (B) Electron microscopy of Gag-GFP particles released from transfected COS-1 cells. (C) Confocal microscopy of QT6 cells expressing GFP alone, Gag-GFP, or M domain mutants of Gag-GFP. (D) Thin sections of QT6 cells expressing 4,5-GFP, with arrows pointing to the electron-dense aggregates in the cytoplasm. (E) Higher magnification of aggregates formed in QT6 cells expressing 3,4-GFP. In all electron micrographs, bars represent 100 nm.