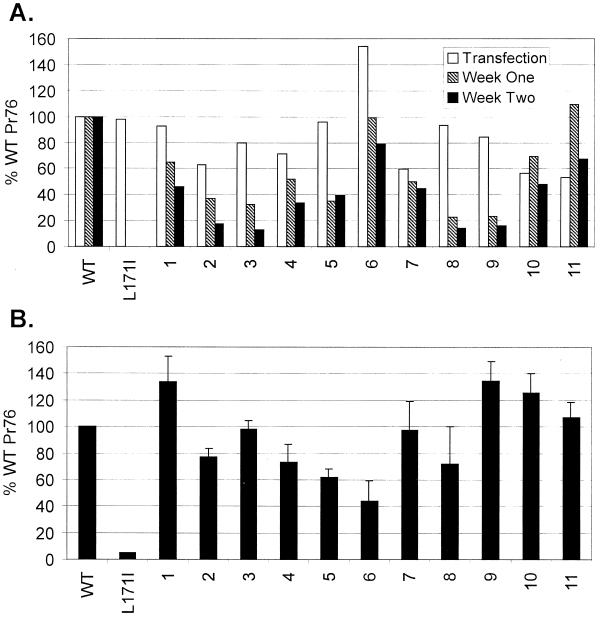
FIG. 5.
Infectivity assays. (A) Virus spreading in transfected cultures. Proviral clones of mutants with neutralizations of single basic residues in the M domain were transfected into avian (QT6) cells. Duplicate cultures were either labeled for 5 min with [35S]methionine 18 h after transfection or were passaged every 3 to 4 days and labeled at 1 and 2 weeks posttransfection. Gag proteins from cell lysates were collected by immunoprecipitation, separated by SDS-PAGE, and quantified by PhosphorImager analysis. Infectivity is expressed as a percentage of the total radiolabeled Gag (Pr76) in the lysates of cells transfected with the wild-type (WT) proviral clone. The negative control has a substitution (L171I) in the MHR of CA that renders extracellular particles noninfectious. Values represent the average of two experiments using independent clones for each mutant. (B) Single-cycle infectivity. TEFs were incubated for 48 h after transfection with proviral DNAs. Virus-containing media were then centrifuged to remove cellular debris, and the supernatants were transferred to uninfected TEFs. After 24 h, these cultures were labeled for 15 min with [35S]methionine, and intracellular Gag (Pr76) expression was quantified after immunoprecipitation and SDS-PAGE. Infectivity was then calculated by normalizing Pr76 levels to the amount of virus in the corresponding inocula. The ability of each mutant to enter cells and produce Gag proteins from integrated genomes is expressed as a percentage of wild-type's efficiency (n = 3, error bars indicate standard deviation).