Figure 6. The CCAR1-U2AF1/2 axis is critical for exclusion of the FANCA poison exon.
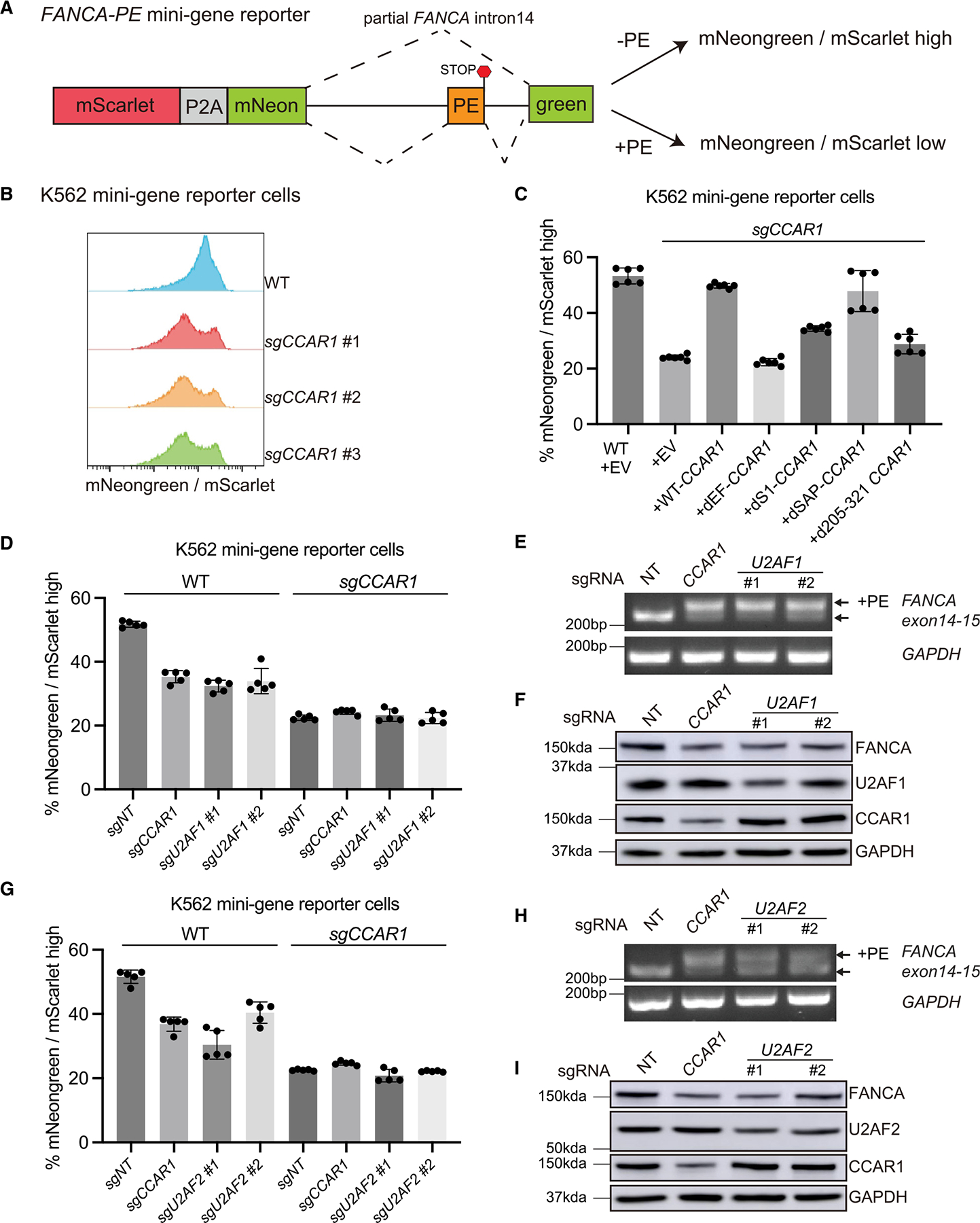
(A) Schematic representation of the fluorescence-based FANCA PE mini-gene reporter. See also Figure S6A.
(B) Histograms showing the ratio of mNeongreen to mScarlet (mNG/mSC) signal from K562 WT and CCAR1 knockout clones carrying the mini-gene reporter.
(C) K562 WT and CCAR1 knockout mini-gene reporter cells were transduced with the indicated lentiviral constructs. Mean and SD of mNG/mSC high cells are plotted (n = 6).
(D and G) Loss of CCAR1, U2AF1, or U2AF2 leads to reduced mNG/mSC indicating splicing defect. K562 WT or CCAR1 knockout mini-gene reporter cells were lentivirally transduced with Cas9 and either non-targeting control sgRNA (sgNT), sgCCAR1, or sgU2AF1 (D), or sgU2AF2 (G). 96 h after puromycin selection, the pool cells were analyzed by flow cytometry, and the mean and SD of mNG/mSC ratio was plotted (n = 5).
(E and H) Loss of U2AF1 or U2AF2 leads to inclusion of FANCA poison exon. RT-qPCR showing evaluation of FANCA poison exon (PE) inclusion in the K562 minigene reporter cells transduced with sgNT, sgCCAR1, sgU2AF1(E), or sgU2AF2(H).
(F and I) Loss of CCAR1, U2AF1, or U2AF2 leads to reduction in FANCA protein levels. Evaluation of FANCA protein levels in K562 mini-gene reporter cells transduced with sgNT, sgCCAR1, sgU2AF1(F), or sgU2AF2(I).
See also Figure S6.
