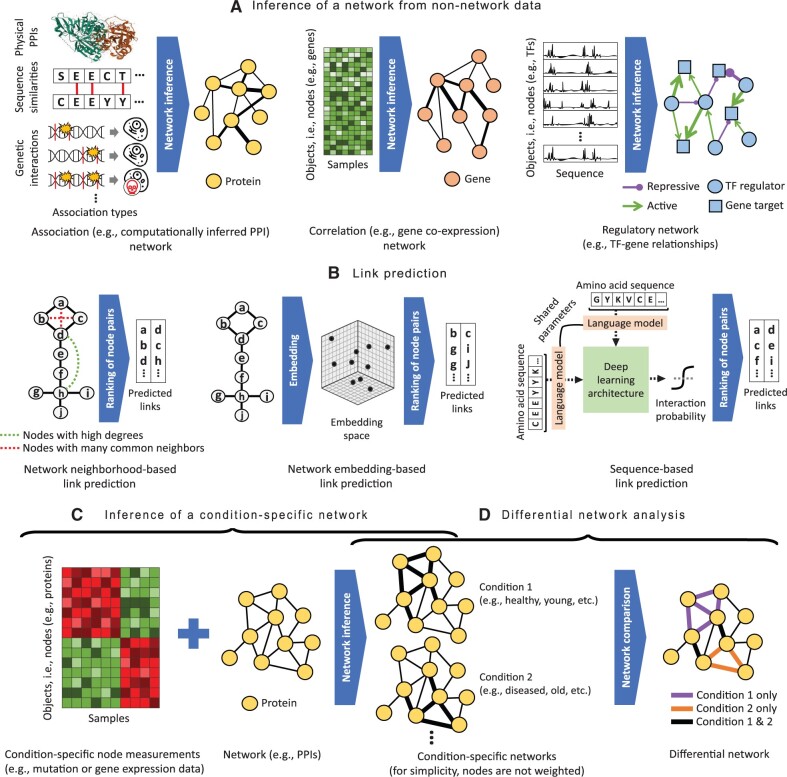
Figure 2.
Prominent topics related to network inference and comparison. (A) Inference of an association (left), correlation (middle), or regulatory (right) network from nonnetwork data. (B) Link prediction: inference of new interactions from existing network data via neighborhood- (left) or embedding-based (middle) approaches, or from sequence data (right). For the former, shown are nodes that may be linked by new edges because two given nodes have high degrees (preferential attachment) or share many common neighbors; other neighborhood-based approaches exist, as discussed in the text. (C) Inference of a condition-specific network. The second approach category is illustrated. The thicker an edge in the network for a given condition, the more relevant the edge is for that condition. (D) Differential network analysis. Illustrated is a potential differential network between conditions 1 and 2, containing edges that are highly relevant for condition 1 but not condition 2, edges that are highly relevant for condition 2 but not condition 1, and edges that have consistent relevance patterns in both conditions.