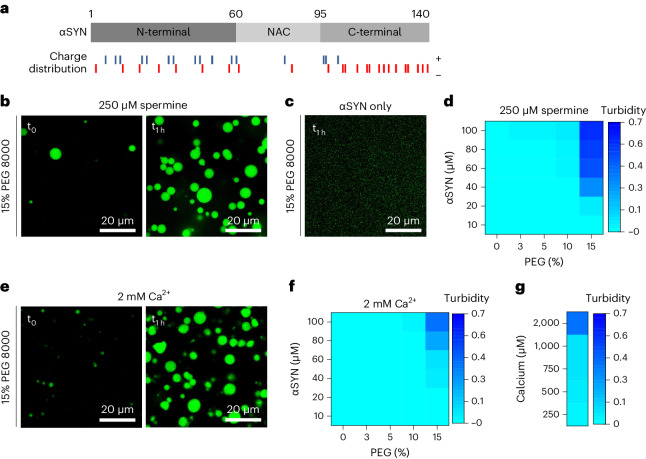
Fig. 1. αSYN undergoes phase separation upon electrostatic interaction.
a, Schematic of αSYN showing its three main protein regions, the N-terminal lipid binding region, the NAC region and the negatively charged C terminus. Charge distribution along αSYN sequence; blue indicates positively charged residues and red indicates negatively charged residues. b, αSYN phase separation in the presence of 250 µM spermine and crowding with 15% PEG 8000, immediately after PEG addition (t0) and after 1 h (t1h). αSYN was used at 100 µM. c, αSYN on its own does not show droplet formation in the presence of 15% PEG 8000. αSYN was used at 100 µM. d, Heatmap showing turbidity measurements of αSYN phase separation in the presence of 250 µM spermine. Data represent three biological repeats. e, αSYN phase separation in the presence of 2 mM Ca2+ and crowding with 15% PEG 8000, immediately after PEG addition (t0) and after 1 h (t1h). αSYN was used at 100 µM. f, Heatmap showing turbidity measurements of αSYN phase separation in the presence of 2 mM Ca2+. Data represent three biological repeats. g, Heatmap for αSYN phase separation in the presence of different Ca2+ concentrations in the presence of 15% PEG 8000. αSYN was used 100 µM. Data represent three biological repeats.