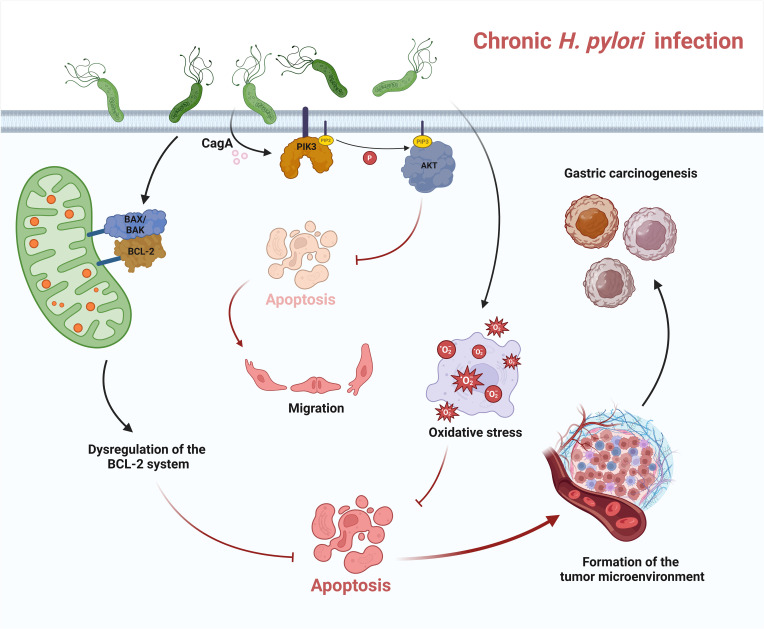
Figure 2.
Apoptosis in chronic H. pylori infection. In chronic infection, H. pylori can trigger dysregulation of the BCL-2 system and downregulate apoptosis. H. pylori also leads to chronic inflammation, triggers oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis. CagA, the virulence factor released by H. pylori, can regulate the activation of PI3K and AKT. AKT-dependent phosphorylation of caspase-9 attenuates apoptosis. All these dysregulations of apoptosis in chronic infection lead to the formation of a tumor microenvironment and ultimately contribute to the development of gastric cancer.