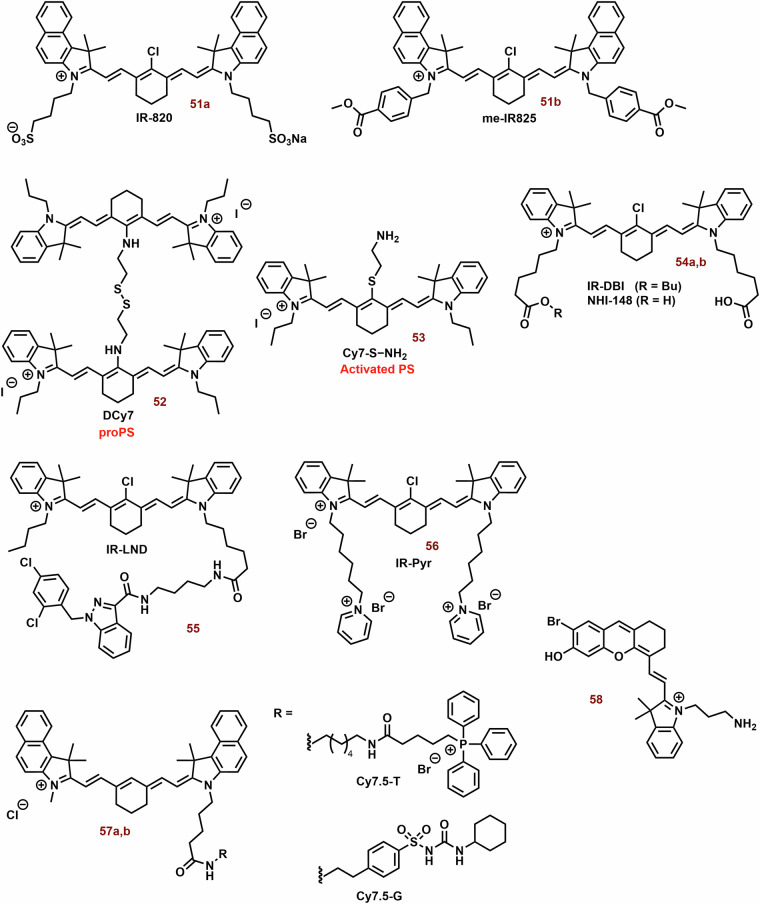
Fig. 20. Photodynamic and photothermal cyanine dyes tested in the form of nanoparticles and biopolymer complexes.
Nanoparticles play a crucial role in augmenting the therapeutic efficacy of various anticancer agents, such as photoactive dyes. In this context, supramolecular systems like liposomes (51a) and polymeric micelles (51b and 52) are extensively studied. Encouraging results have also been demonstrated with the biopolymer application of serum albumins (54a, 54b, and 55) and hyaluronic acid (56). Additionally, inorganic nanoparticles such as molybdenum disulfide nanoflakes (57a, 57b) and Ag2S quantum dots (58) have shown promise in this area. Compounds like 52 and 55 exhibit other anticancer activities, such as reducing glutathione levels (a defense against oxidative stress) and inhibiting oxidative phosphorylation, respectively. Notably, in the case of the no-active compound 52, its reaction with glutathione results in the release of active PS 53.