Figure 4.
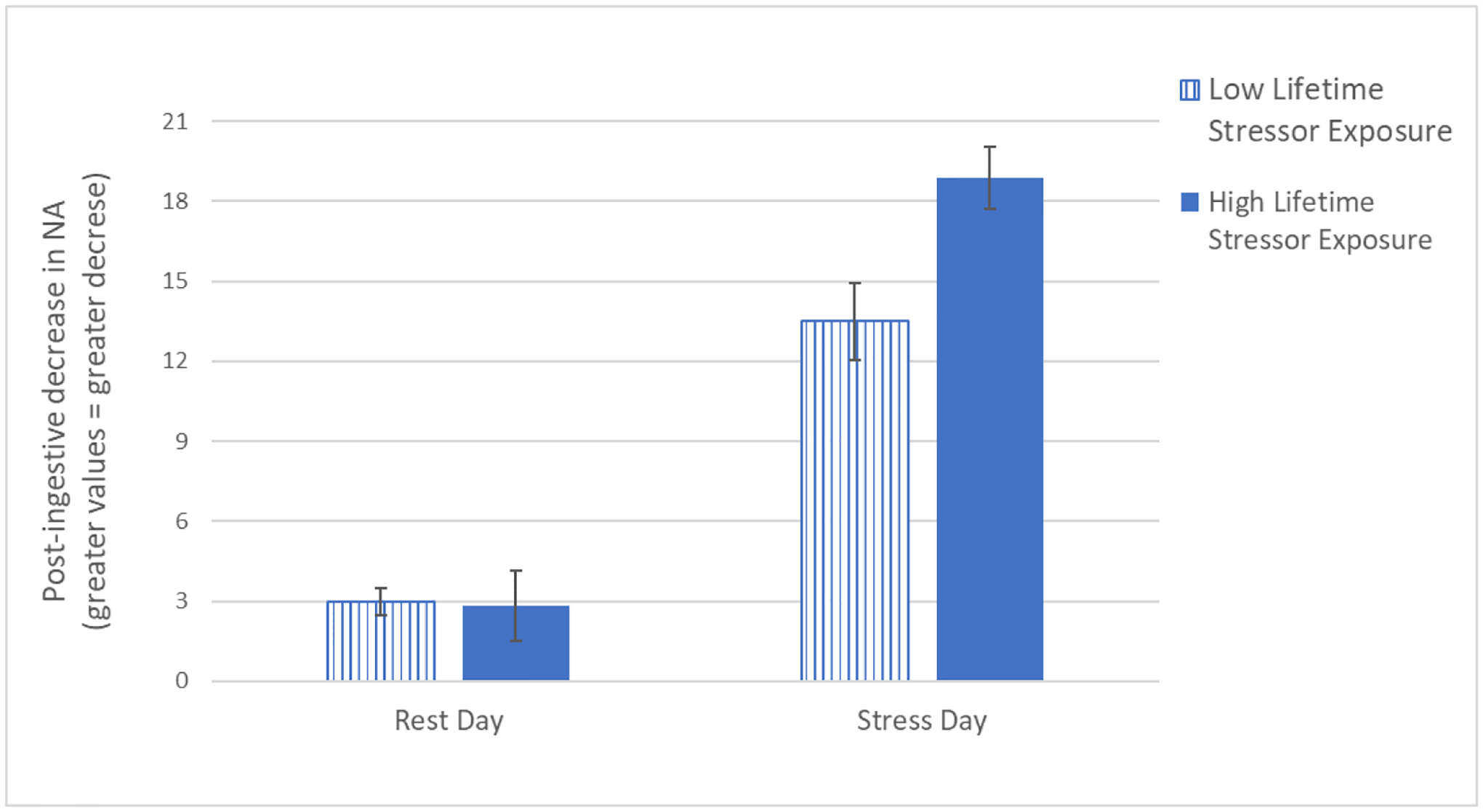
Visual depiction of the linear regression analyses predicting post-ingestive reductions in negative affect (NA) following rest and the laboratory-based acute social stressor. We split the continuous lifetime stressor exposure variable into Low and High using 1 standard deviation above and below the mean, and used the formula: y = a +b1*x + b2*x +b3* x + b4*x. Experience more lifetime stressors was related to greater post-ingestive reductions in negative affect, but only on the stress day, F(4, 21) = 4.03, p = 0.01, R2 = 0.43.
