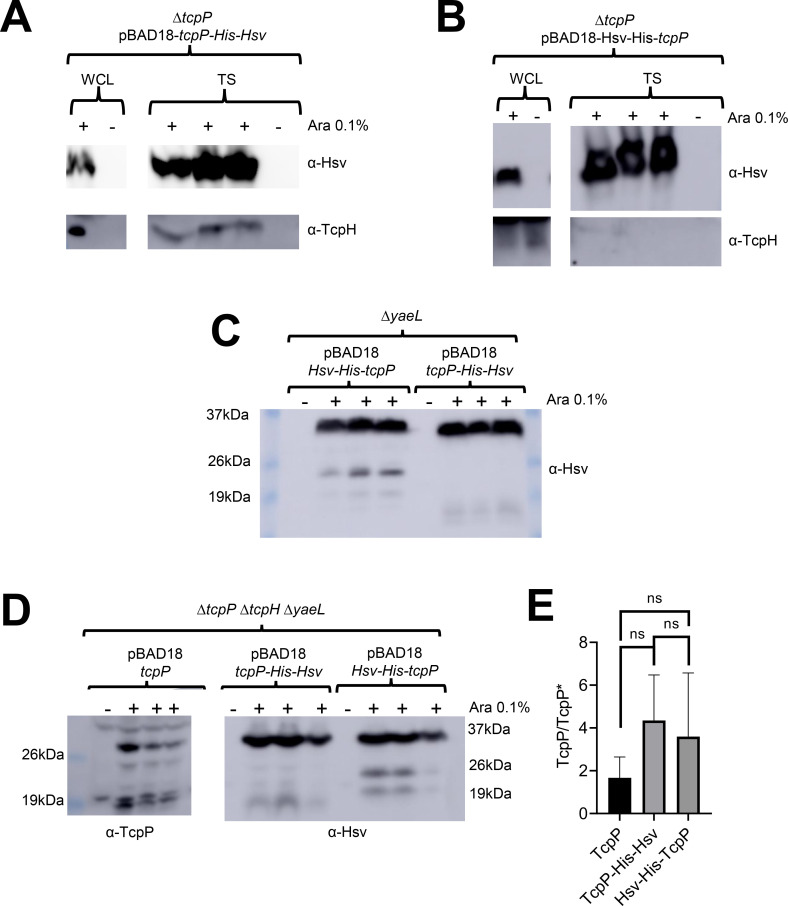
Fig 5.
TcpP and TcpH interaction is critical for TcpH-dependent inhibition of RIP. (A and B) Co-affinity precipitation of ectopically expressed tcpP-His-HsV (A), Hsv-His-tcpP (B). Triton soluble (TS). (C) Ectopic expression of Hsv-His-tcpP and tcpP-His-HsV in ΔyaeL cells under virulence-inducing conditions. Hsv-His-TcpP is more sensitive to RIP than TcpP-His-Hsv, as seen by the accumulation of TcpP degradation intermediates between 26 and 19 kDa. (D) Ectopic expression of tcpP and tcpP-His-HsV in ΔtcpP ΔtcpH ΔyaeL cells under virulence inducing conditions. Samples were probed with α-TcpP (left) and α-Hsv (right) antibodies. (E) The ratio of full-length TcpP (29 KDa) to other TcpP degradation products (i.e., TcpP*) in western blots found in panel D. Abundance of full-length TcpP and TcpP* was determined via densitometry, using ImageJ. ns, indicates no statistical significance. A one-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance. (A–D) tcpP constructs were all ectopically expressed from pBAD18 using arabinose (Ara 0.1% wt/vol). +indicates arabinose was added to the culture. The data here represent samples collected from three independent experiments.